Table of Contents
Software as a Service, abbreviated as SaaS, is a licensing software and delivery model in which the software is licensed on a subscription basis. SaaS is a centrally hosted software which is also known as web-hosted/web-based or software on demand. It is considered as the part of cloud computing with an Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Desktop as a Service (DaaS, Platform as a Service (PaaS), Software Managed as a Service (MSaaS), Data Center as a Service (DCaaS), etc.
The users of the SaaS applications usually access them through a thin client such as a web browser. SaaS has become a common delivery model for a lot of business applications such as email software, office software, DBMS software, management software, payroll software, CAD software, etc. SaaS has been integrated into the strategy of almost every enterprise software company. It is predicted that it will remain one of the largest market segments for public cloud services.
History of SaaS
The advent of cloud computing made it possible to install software on remote offsite servers. In some cases, they were maintained by third parties. Cloud computing made it possible to reduce the amount of maintenance required and enabled a better and increasing global workforce, as software. Mostly, it was possible due to the software being accessible from anywhere.
Over time, there have been improvements on the internet that have reduced the cost of hosting. Also, it led the platforms to remove most of the initial bandwidth limitations. Hence, making the online business process more reliable and faster.
Improvements in core functionality, ease of use, and cost-efficiency led to exponential growth in SaaS. Today, SaaS is a practical option even at the enterprise level.
Beginning of SaaS
In the 1960s, computer hardware technology was advancing rapidly. However, IT was still time-consuming and the cost of a mainframe was prohibited for many organizations. It is where time-share comes in. A Compatible Time-Sharing System (CTSS) was developed at MIT and was first found to be effective in 1961 [1].
Pre-SaaS Computing
Over the next 20 to 30 years, computing and hardware became cheaper and more portable. It was at this point that companies moved to individual ownership such as on-premise software installed on personal computers or other machines under a purchased license. On the other hand, local software has proven ineffective on a large scale for both the IT staff who run it and the software companies who sell it.
IT has become bogged down in software installations, security patches, updates, and maintenance of the company’s computer infrastructure and hardware. The companies have lower margins due to the cost of goods sold (COGS) and the costs of distributing the software on disks in product packaging [2].
Dot-com Boom
In August 1994, the internet took a big step forward in terms of online transactions, online business, online cloud, etc.
Online transactions
Daniel Kohn made the first secure credit card transaction for physical goods such a CD Sting. It was said that the government and industrial organizations are working to develop the standard for the automated encryption of business transaction data [3]. A small group of recent college graduates formed the Net Market Company in New Hampshire to be the first and successful implementation of online transactions.
From there, everything e-commerce as we know it today started to happen very quickly. In October 1994, Netscape Navigator introduced the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol to enable encrypted transmission of data over the Internet. As a result, people were able to shop without worrying about losing the data of their bank account.
Online Markets
On September 3, 1995, the launch of Amazon by Jeff Bezos and AuctionWeb by Pierre Omidyar, now known as eBay, was the premier peer-to-peer auction market. By the end of 2000, although it had started as an e-commerce platform for books, Amazon branched out into other product categories [4]. Also, they allowed third-party sellers to sell their products on their online platform.
Online Cloud
The Internet got the boom from the rise of cloud computing. This made it possible to install software on the remote servers, which in some cases, third parties used to maintain them. As a result, the amount of maintenance was reduced and enabled a better and increasing global workforce. It is because the software in the cloud was accessible from anywhere.
These feature enhancements started a movement towards top software vendors. They focused on the good core function such as enabling the organizations to go online and use the software for each function. Hence, it worked best for their business.
SaaS Is Officially Here
In 1999, Salesforce launched its Customer Relationship Management (CRM) platform as the first SaaS solution. It was designed from the ground up for record growth. This turned out to be a good investment, as the dot-com crash of 2001. By the Great Recession, it saw significant success in local software.
In the beginning, the SaaS model was designed for small businesses and startups, which were unstable or too slow. Over the next several years, improvements on the internet that did not matter much to the traditional software industry proved to do a lot for SaaS.
Also, SaaS subscription software was not supposed to be viable for businesses. Indeed, at that time, the company generally opted for end-to-end software packages that were able to manage complex organizations.
What Is SaaS?
SaaS platforms make software available to the users over the internet, typically on a monthly subscription. With SaaS, you don’t have to install and run any software application on the computer. Everything is available on the Internet through the web browser when you log into your online account. Generally, the software can be accessed from any device at any time but make sure that there is an internet connection.
The same goes for anyone else who uses the software. All the employees have personalized login with their level of access. With SaaS, you don’t have to hire an IT specialist who will download the software to multiple computers in the office. Also, there is no need to worry about keeping the software up-to-date. Everything is solved in the cloud.
Another key difference is the business model. For pricing, most SaaS providers use a tiered subscription model with fixed and included monthly account fees. Most subscriptions include security services, compliance, and maintenance, which otherwise can be expensive and time-consuming.
SaaS providers also offer out-of-the-box solutions that are easy to configure, especially for large organizations having complex operations or solutions. You can have basic software up and running within hours. Also, you will have access to customer support and service along the way [5].
Working of Software As A Service

SaaS Characteristics
A good way of understanding the SaaS model is to think of a bank. It protects the privacy of each customer while providing a secure and reliable service at a scale. All the bank customers use the same financial systems and technology without worrying about unauthorized access to their personal information. A SaaS model is based on the key characteristics of the bank.
Multi-User Architecture
A multi-user architecture, in which all the applications and users share a single common infrastructure and a centrally managed codebase. The SaaS vendor customers all use the same codebase and infrastructure, where vendors can innovate a safer and faster development.
SaaS Leverages The Mainstream Web
Anyone familiar with My Yahoo and Amazon.com will be familiar with the web interface of typical SaaS applications. With a SaaS model, one can customize the point-and-click ease making the weeks or months to update the traditional business software that seemed hopelessly out of date.
Easy Customization
The ability for each user to easily customize applications according to the business processes without affecting the common infrastructure. The way the SaaS is designed, there are unique customizations to each user and company which are always preserved during the updates. This means SaaS providers can upgrade more frequently with less risk to the customer and a much lower cost of adoption.
Better Access
Better access to data from any networked device while making it easier to manage privileges, ensuring that everyone sees the same information at the same time, and monitoring data usage.
SaaS Trends
Organizations are now developing SaaS or SIP integration platforms to build additional SaaS applications. Consulting firm Saugatuck Technology calls it the third wave of software adoption. When SaaS goes beyond stand-alone software functionality to become a platform for mission-critical applications [6].
Advantages & Disadvantages of SaaS
Advantages of SaaS
Accessibility
A big advantage of any SaaS application is the ability to run through an internet browser. It does not depend on the operating system you are using to access it. So, you can run the SaaS applications on Windows, Mac, or Linux machines or sometimes iOS or Android smartphones. Hence, it makes SaaS applications incredibly versatile in various ways.
On the other hand, SaaS applications can not only be used in the office on desktops but also on mobile devices such as tablets. The purpose of SaaS is to create mobile-friendly applications that can be used in a wide range of circumstances and situations, on the go.
Hardware
This leads to one of the other main selling points of SaaS which is the lack of upfront investment required to use it. In the case of on-premise software, sometimes it is not only the corporate PCs or other desktops that have compatible software and hardware configurations but additional networks and server switches that might be required in the fields. Overall investment in the IT infrastructure services is required to support the software throughout the company.
SaaS eliminates this need. It means that even the smallest businesses can now access the software tools through SaaS-based cloud applications. Also, SaaS is scalable in the sense that if you need to add more users to the service or reduce them, you can simply adjust the billing plan accordingly. Instead of buying more hardware while expanding and having to shelve expensive equipment while reducing, you can simply choose the right billing plan for your business operations.
Cost Savings and Storage
On-premise data storage you have to invest in reliable backups such as disaster recovery plans or cloud storage. It mitigates any serious hardware failure that could lead to the failure such as significant data loss.
However, with SaaS, data is regularly saved in the cloud. It makes a double benefit such as not only the redundancy aspect but also the fact that employees can switch between the device without losing data. Simply, they have to log in to their designated account.
Updates and Patches
Another key benefit of SaaS applications is that they can run in the cloud which can be updated by the vendors without affecting the users’ business operations. This is in stark contrast to on-premise software which requires some degree of endpoint compatibility and security testing before routine updates and patches can be applied.
Therefore, the SaaS model avoids testing the pitfalls that slow down the development cycle and access to new features for the users. Meanwhile, it is ensured that the security updates are applied as soon as possible, unlike local software that may remain vulnerable. Otherwise, there can be an attack on the business operations until IT service management personnel have completed their testing.
Market Reach
For vendors, market reach or scope means being able to offer a software service to the majority of the market rather than limiting their customers to one business or specific market segment. For every business of all sizes, the prices can be cheaper or expensive. For the users, it means that they can access the services that are normally not available to them.
Hence, they can improve their business productivity, services and avail themselves of new opportunities while using SaaS applications.
Data And Analytics
Because everything goes through a centralized platform, it means that it is easy to capture data and deliver it for analytical purposes. Companies using SaaS software typically have access to intelligence and reporting tools and visualizations that can provide valuable insight into business operations. It allows better workflows and efficiency savings.
For the provider, the access is dependent on the paid subscription, so they don’t have to worry about hacking which could otherwise be costly to the provider while damaging the pricing models and access [7].
Disadvantages of SaaS
Lack of Control
The internal software applications provide businesses with a greater degree of control than hosted solutions. It is because the third party is having control of the SaaS applications. Normally, everyone should be using the latest version of the software application that cannot defer feature changes or updates.
Performance
SaaS might run slower than on-premise server applications. It depends on the internet connection that can cause lag in operations due to internet connection interruption. Therefore, most businesses prefer performance over cost and other aspects because the software is not hosted on the local machine.
Security and Data Issues
Managing access and privacy of sensitive information is sometimes one of the most important considerations. In the case of SaaS applications, sometimes the threat of security and data becomes a bigger issue than it seems to be.
Connectivity Requirement
Since the SaaS model is webcast-based, if the internet connection fails, it means you will lose access to the data or software.
Limited Range of Applications
SaaS has become popular over the years but still, some applications do not offer a hosted platform. It creates a major issue for all kinds of businesses operating on SaaS applications [9].
SaaS Security and Privacy
The cybersecurity risks associated with SaaS are different from the risks associated with traditional software. With traditional software, the software vendor is responsible for covering up the code-based vulnerabilities, whereas, the user is responsible for running the software on a secure infrastructure and network. As a result, security is a major responsibility of the independent software vendor and the third-party cloud vendor.
Despite the adoption of the cloud-based models for full-service software products, when it comes to security and privacy, some organizations are still having reservations about the SaaS products [10].
- Encryption and Key Management
- Security Monitoring
- Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Response to the Incident
- Lack of communication with security and technician experts during the sales process
- The cost of investing in third-party tools to offset the security risk of SaaS
- Poor integration into larger, company-specific security environments
- Data confidentiality
- Compliance with data residency requirements
SaaS vs. IaaS vs. PaaS
Figure 3: Diagram of an easy example to understand the difference between SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS.
SaaS is one of the three main models of cloud services along with IaaS and PaaS. All three models involve cloud providers who deliver the hosted data center resources to customers over the internet. Where the models differ is in the integrity of the product. SaaS products are fully managed applications. IaaS heavily outsourced data center resources, whereas, PaaS offers development and other tools platforms hosted in the vendor’s data center [12].
SaaS
Users of SaaS applications do not have to:
- Download the software
- Take care of any aspect of the software management
- Manage an existing IT
In this case, security, support, updates, and maintenance are done by the vendors.
IaaS
IaaS is used by those companies who want to outsource their IT resources and data center to a cloud provider. Infrastructure components are hosted by the IaaS providers such as:
- Virtualization resources
- Networking hardware
- Storage
- Servers
On the other hand, the customer organizations operating on IaaS services must always manage their use of data, operating systems (OS), and applications.
PaaS
PaaS provides a framework of resources for internal developers of an organization. The hosted platform in PaaS allows the developers to build their custom applications. The provider of PaaS applications manages the data center resources while supporting the tools. Also, the customer organizations using PaaS services have to manage the application and data usage rather than managing their operating systems.
Figure 4: Data by KPMG [13]
Team Collaboration
Team collaboration is of great importance to any business, especially on remote working days. SaaS tools give a better overview and better understanding of what the team members are doing. Also, it is a crucial tool for increasing productivity by allowing the teams to work efficiently. Additionally, a SaaS tool uncovers the strengths and weaknesses of the business while empowering you to make improvements.
Website Creation And Online Forms
Building a website is not a piece of cake. If you want to avoid the complexity of manual coding, there are powerful SaaS website builder tools that allow users to easily build websites and forms. Also, SaaS cloud-based website builder tools allow users to easily edit websites from any location.
Automated Billing Systems
Money management is a sensitive department. Billing and invoicing should be smooth and accurate to provide a secure shopping experience for the customers. Manual solutions can cause problems for the business as the business grows and scales. An automated billing system can help you to avoid wasting time on the business finances and spending it on other areas of the business.
Customer Support
Customers are the lifeline of the business. A business can keep them satisfied with quality products and after-sales service. Customer Relationship Management software can simplify the complex and cumbersome process. Also, it can organize the contact information and help to manage the current relationships with the potential customers.
IT Security
A business faces multiple security challenges in the form of online fraud, phishing, and other online threats. Computer security software can combat those threats and protect the critical data of the business such as finances. If you are not using a dedicated SaaS security software, then there are fair chances of a security breach that can cost your business a lot of money [15].
SaaS By Numbers
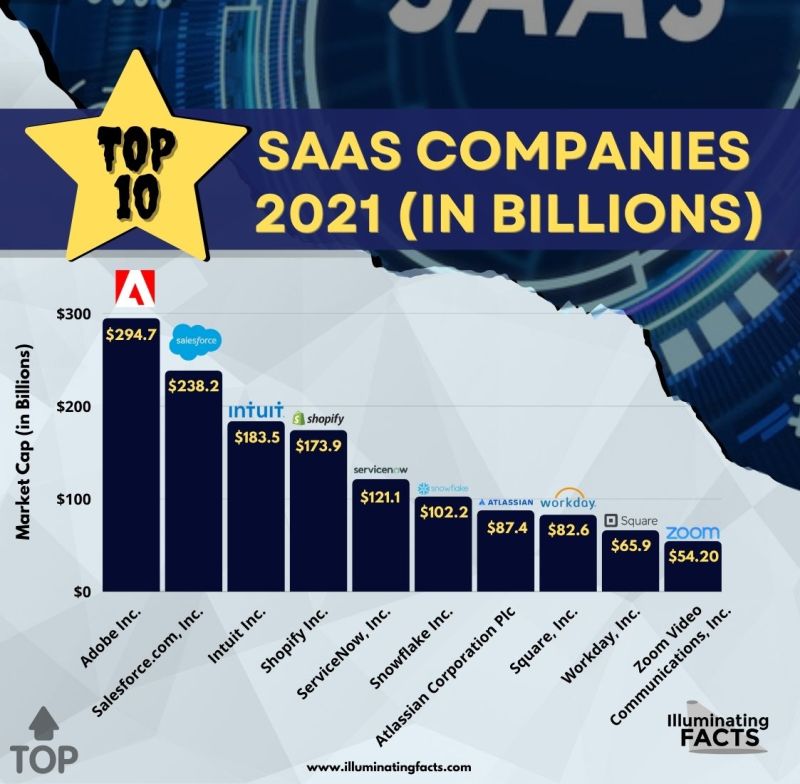
50 Biggest SaaS Companies
There are the 50 biggest SaaS companies according to the market capitalization of the U.S. Stock Exchanges. The list has been defined based on revenue of more than 65 percent that is attributed to recurring payments for cloud-based software.
| Company | Market Cap (in Billions) |
| Adobe Inc. | $294.70 |
| Salesforce.com, Inc. | $238.20 |
| Intuit Inc. | $183.50 |
| Shopify Inc. | $173.90 |
| ServiceNow, Inc. | $121.10 |
| Snowflake Inc. | $102.20 |
| Atlassian Corporation Plc | $87.40 |
| Square, Inc. | $82.60 |
| Workday, Inc. | $65.90 |
| Zoom Video Communications, Inc. | $54.20 |
| Cloudflare, Inc. | $51.40 |
| Datadog, Inc. | $50.60 |
| CrowdStrike Holdings, Inc. | $44.50 |
| Zscaler, Inc. | $42.90 |
| Unity Software Inc. | $42.50 |
| Twilio Inc. | $42.00 |
| Veeva Systems Inc. | $38.20 |
| HubSpot, Inc. | $34.80 |
| Okta, Inc. | $32.80 |
| MongoDB, Inc. | $28.00 |
| DocuSign, Inc. | $26.30 |
| Paycom Software, Inc. | $25.10 |
| ZoomInfo Technologies Inc. | $22.30 |
| Bill.com Holdings, Inc. | $22.10 |
| Splunk Inc. | $19.00 |
| Qualtrics International Inc. | $18.60 |
| Akamai Technologies, Inc. | $18.10 |
| RingCentral, Inc. | $17.60 |
| Dynatrace, Inc | $16.80 |
| Ceridian HCM Holding Inc. | $15.90 |
| Paylocity Holding Corporation | $13.40 |
| F5 Networks, Inc. | $13.40 |
| Bentley Systems, Incorporated | $12.90 |
| Coupa Software Incorporated | $12.50 |
| monday.com Ltd. | $12.10 |
| Avalara, Inc. | $11.60 |
| Zendesk, Inc. | $11.50 |
| Asana, Inc. | $11.00 |
| Procore Technologies, Inc. | $10.50 |
| Elastic N.V. | $10.10 |
| Citrix Systems, Inc. | $9.90 |
| Dropbox, Inc. | $9.40 |
| Guidewire Software, Inc. | $9.00 |
| DigitalOcean Holdings, Inc. | $8.90 |
| Five9, Inc. | $8.60 |
| Smartsheet Inc. | $8.30 |
| Wix.com Ltd. | $8.10 |
| New Relic, Inc. | $6.60 |
| The Descartes Systems Group Inc. | $6.50 |
| Workiva Inc. | $6.40 |
Figure 6: Data by MikeSonders [16]
Figure 7: Data by MikeSonders [17]
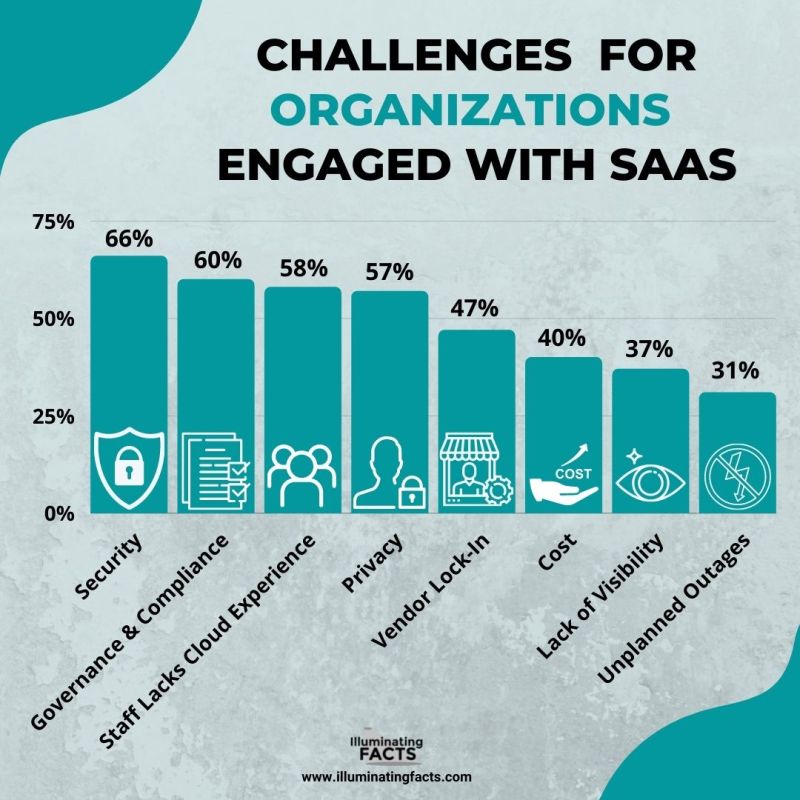
Challenges for Organizations Engaged with SaaS
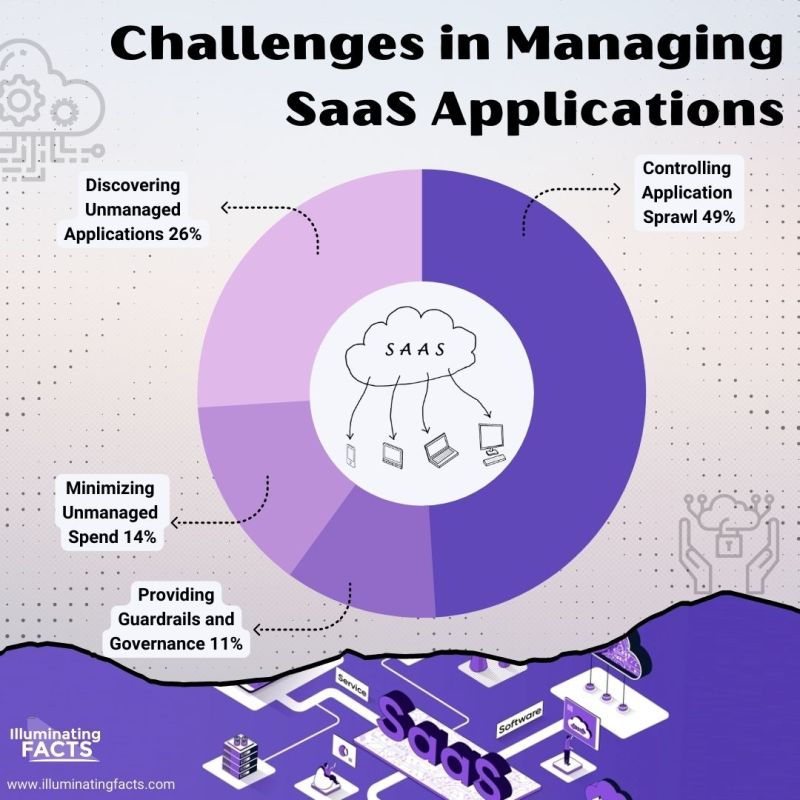
In 2021, IT leaders in organizations of 500 or more employees declared that the biggest challenge in their organization was to manage Software as a Service (SaaS). On the other hand, half of them were worried about the controlling application expansion in the organization [18].
Figure 8: Data by Snowsoftware [19]
Figure 9: Data by FinancesOnline [20]
On the other hand, as a solution to the challenges, the IT leaders in such organizations relied more on Zoom, Google Workspace, and Microsoft 365. In their point of view, these SaaS applications are more impactful than any other.
| Reliable Tools | Applications |
| Cloud Infrastructure | Microsoft Azure
AWS Google Cloud |
| Office Suites | Office 365
Dropbox Paper G Suite |
| Specialty Software | Salesforce
Adobe |
Figure 10: Data by Snowsoftware [21]
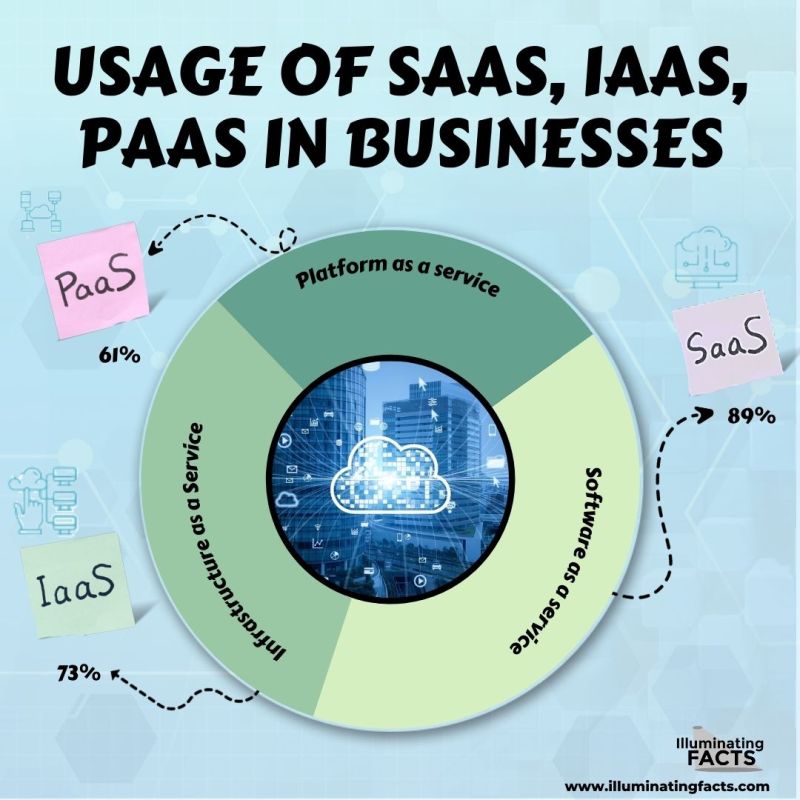
Businesses Using SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS
Figure 12: Data by FinancesOnline [23]
Figure 14: Data by Flexera [25]
SaaS Churn Statistics
Logically, it is assumed that the longer the contract between the vendor and customer of SaaS, the lower the churn rate. If the contract is for less than a year, the higher the dropout rate such as 16.7%. On the other hand, when the contract is for 2.5 to 3+ years, it is almost halved to 8.5%. Hence, if you are unable to get a contract of 2 years or more, a month-to-month contract can keep the churn rates low.
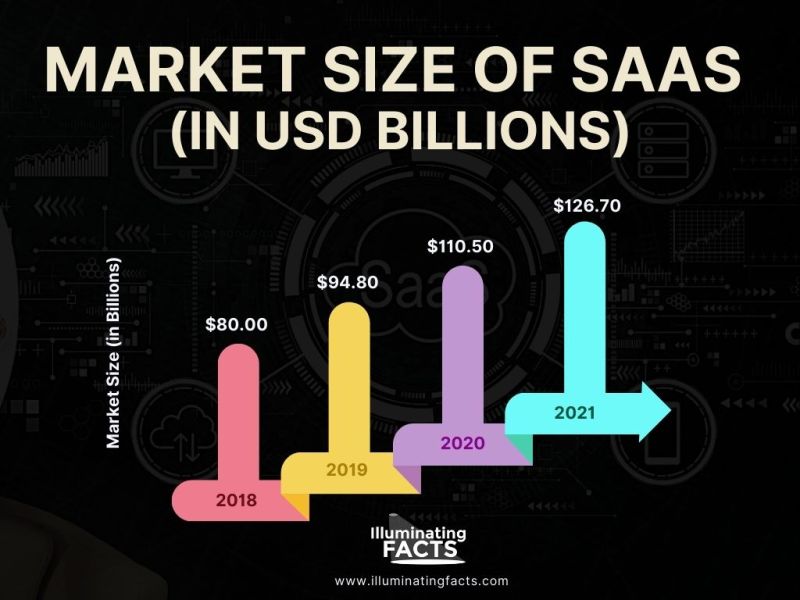
SaaS Market Size (2018 – 2021)
Different projects over the years have clearly stated that the SaaS market will grow in the years to come. By the end of the year 2021, the SaaS market size is expected to reach the value of $272.49 billion with 20.8% of the CAGR. In the next 5 years, the value of the SaaS market size is expected to reach $436.9 billion with 12.5% of CAGR.
Figure 17: Data by SaaSworthy [28]
Projects Delivered On Time By SaaS Companies Worldwide, 2015 to 2020
The project delivery on time by professional services within the software as service companies have been more than 70 from 2015 to 2020. During 2020, an average 75 percent on-time delivery of projects was reported by the SaaS professional services firms, worldwide.
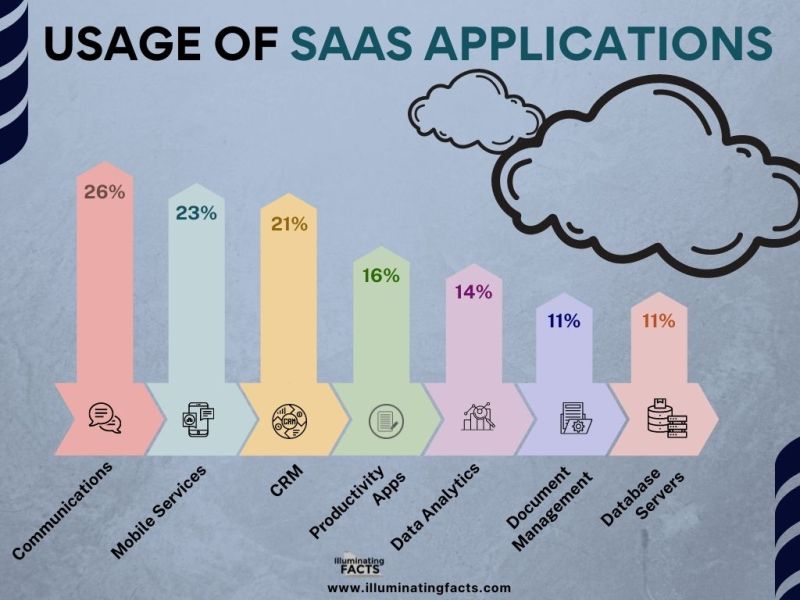
Usage of SaaS Applications in Different Departments
Figure 20: Data by CustomerThink [31]
Interesting Facts about SaaS
- In the 1960s, computer hardware technology was advancing but IT was still time-consuming and costly.
- In August 1994, the internet took a step towards the online cloud, online business, online transactions, etc.
- Salesforce launched its Customer Relationship Management (CRM) in 1999. It was the first SaaS solution.
- SaaS platforms make software available to users over the internet on a monthly subscription.
- Improved Agility and responsiveness are some of the major advantages of SaaS applications.
- Encryption of an organization’s data is one of the major threats of SaaS applications used worldwide.
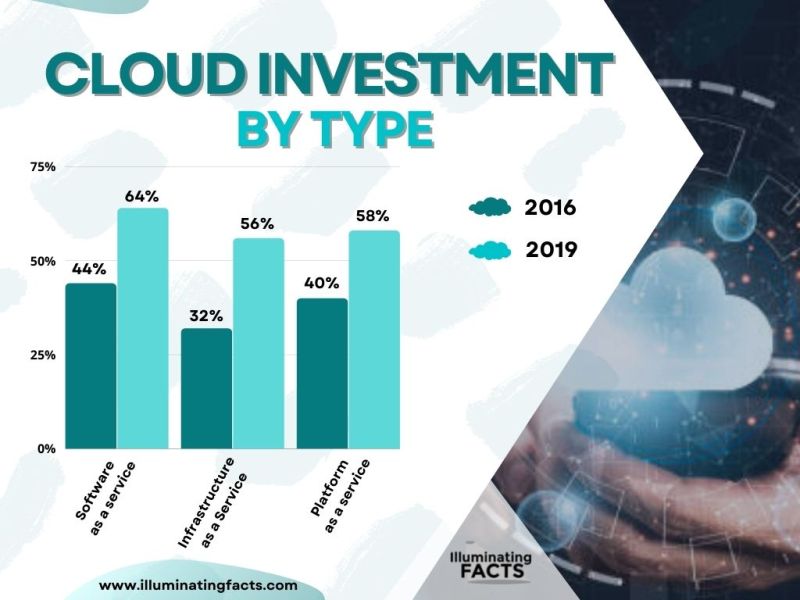
- Since 2016, there has been more cloud investment in SaaS than IaaS and PaaS. It was 64% in 2019 in SaaS, which is 8% and 6% more than investment in IaaS and PaaS, respectively.
- Adobe stands first in the list of 50 biggest SaaS companies with a market capitalization of $294.70 billion (2021).
- Organizations engaged with SaaS applications face security challenges at 66% which is the highest in all challenges.
- Despite all the shortcomings, SaaS is still the most used application or cloud platform in all kinds of businesses.
- In the public cloud, the adoption rate of the Website is 55% among other applications.
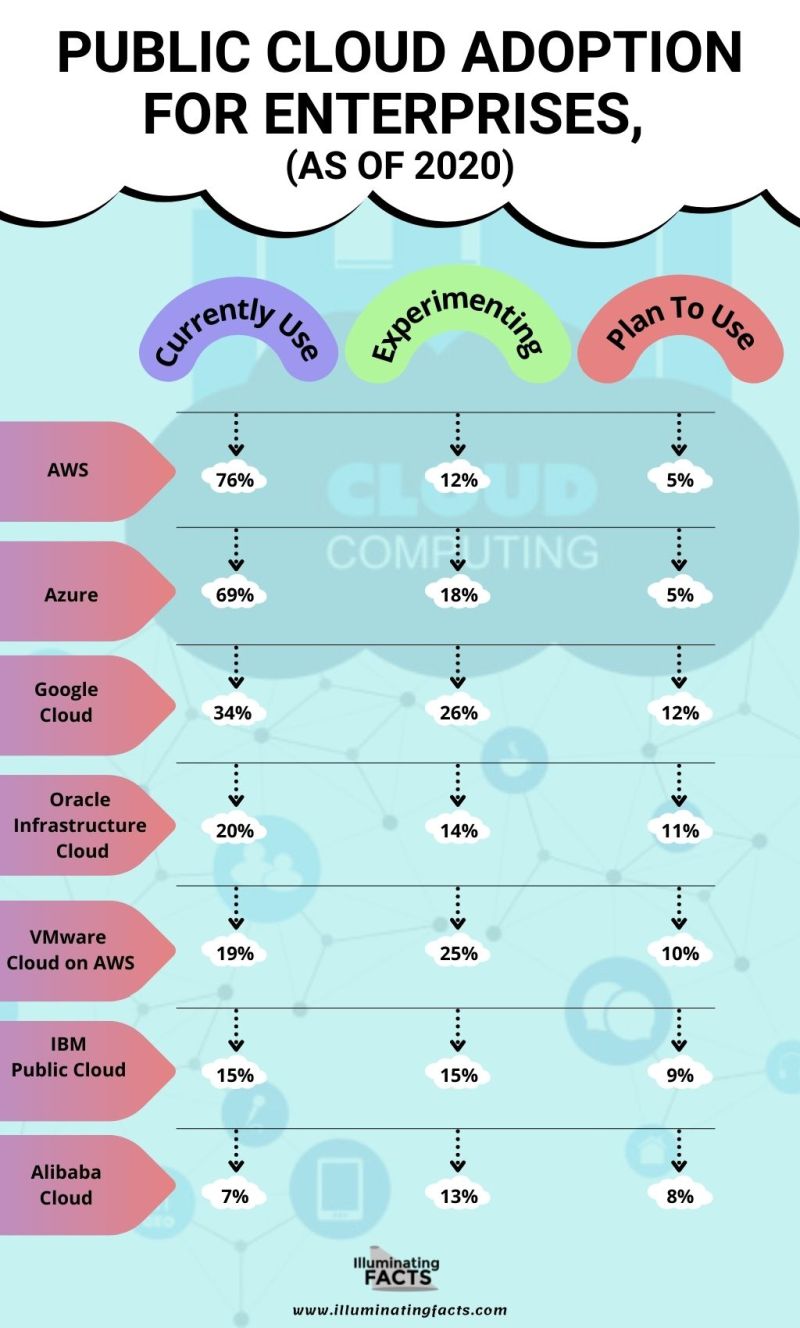
- Some enterprises are still working on the adoption, experimentation, and planning of SaaS applications.
- The best option to get a contract with a lower dropout rate is a month-to-month contract that gives an average 14% annual gross dollar churn rate.
- The market size of SaaS was $80 billion in 2018. Since then, it has grown to $110.50 billion with 20.8% of CAGR in 2021.
- By the end of 2021, the expected market size of SaaS is $272.49 billion with a 20.8% CAGR.
- In the next 5 years, the expected market size of SaaS can reach up to $436.9 billion with 12.5% of CAGR.
- Since 2015, the project delivery on time using SaaS applications has increased to 75% worldwide.
- In 2022, the end-user spending forecast for SaaS is $145,377 million.
- An average firm of 250 employees uses more than 100 SaaS applications.
- In 2021, it is expected that 83% of the organization’s work will be done by SaaS applications.
References
[1] Walden, D., & Vleck, T. (2011). Compatible Time-Sharing System (1961-1973) Fiftieth Anniversary Commemorative Overview [Ebook] (1st ed., p. 7). IEEE Computer Society. Retrieved from https://multicians.org/thvv/compatible-time-sharing-system.pdf?_ga=2.126625161.504589292.1638718646-1303554245.1638536347
[2] Brandall, B. (2017). The Needlessly Complex History of SaaS, Simplified. Retrieved 6 December 2021, from https://www.business2community.com/business-innovation/needlessly-complex-history-saas-simplified-01909462?_ga=2.231533083.504589292.1638718646-1303554245.1638536347
[3] Lewis, P. (1994). Attention Shoppers: Internet Is Open (Published 1994). Retrieved 6 December 2021, from https://www.nytimes.com/1994/08/12/business/attention-shoppers-internet-is-open.html?_ga=2.230893851.504589292.1638718646-1303554245.1638536347
[4] Choosing the Best Ecommerce Platform (Solution Comparison). Retrieved 6 December 2021, from https://www.bigcommerce.com/articles/ecommerce/ecommerce-platforms/
[5] Fryer, V. The History of SaaS and the Revolution of Businesses. Retrieved 6 December 2021, from https://www.bigcommerce.com/blog/history-of-saas/#what-is-saas
[6] What is Software as a Service (SaaS): A Beginner’s Guide. Retrieved 6 December 2021, from https://www.salesforce.com/in/saas/
[7] Turner, B. (2020). What is SaaS? Everything you need to know about Software as a Service. Retrieved 6 December 2021, from https://www.techradar.com/news/what-is-saas
[9] Advantages and disadvantages of Software as a Service (SaaS) | nibusinessinfo.co.uk. Retrieved 6 December 2021, from https://www.nibusinessinfo.co.uk/content/advantages-and-disadvantages-software-service-saas
[10] Chai, W. (2021). What is SaaS (Software as a Service)? Everything You Need to Know. Retrieved 6 December 2021, from https://searchcloudcomputing.techtarget.com/definition/Software-as-a-Service
[12] Chai, W. (2021). What is SaaS (Software as a Service)? Everything You Need to Know. Retrieved 6 December 2021, from https://searchcloudcomputing.techtarget.com/definition/Software-as-a-Service
[13] Journey to the cloud – The creative CIO Agenda. (2017). Retrieved 6 December 2021, from https://assets.kpmg/content/dam/kpmg/xx/pdf/2017/02/the-creative-cios-agenda-journey-to-cloud.PDF?_ga=2.134489589.504589292.1638718646-1303554245.1638536347
[15] Kashyap, V. Top 17 SaaS (Software as a Service) Applications To Help Businesses Grow. Retrieved 6 December 2021, from https://www.proofhub.com/articles/saas-applications
[16] The 50 Largest Public SaaS Companies in 2020. (2021). Retrieved 6 December 2021, from https://www.mikesonders.com/largest-saas-companies/
[17] The 50 Largest Public SaaS Companies in 2020. (2021). Retrieved 6 December 2021, from https://www.mikesonders.com/largest-saas-companies/
[18] Challenges surrounding SaaS apps worldwide 2021 | Statista. (2021). Retrieved 6 December 2021, from https://www.statista.com/statistics/1267901/saas-apps-biggest-challenges-organizations-worldwide/
[19] Austin, R. (2021). Study: Hybrid Work Is Here to Stay, Bringing Its Own Mix of Complexities. Retrieved 6 December 2021, from https://www.snowsoftware.com/blog/study-hybrid-work-here-stay-bringing-its-own-mix-complexities
[20] Gilbert, N. (2021). 12 SaaS Trends for 2021/2022: New Forecasts You Should Know – Financesonline.com. Retrieved 6 December 2021, from https://financesonline.com/saas-trends/
[21] Austin, R. (2021). Study: Hybrid Work Is Here to Stay, Bringing Its Own Mix of Complexities. Retrieved 6 December 2021, from https://www.snowsoftware.com/blog/study-hybrid-work-here-stay-bringing-its-own-mix-complexities
[23] Gilbert, N. (2021). 12 SaaS Trends for 2021/2022: New Forecasts You Should Know – Financesonline.com. Retrieved 6 December 2021, from https://financesonline.com/saas-trends/
[25] 2020 State of the Cloud Survey from Flexera. (2020). Retrieved 6 December 2021, from https://info.flexera.com/SLO-CM-REPORT-State-of-the-Cloud-2020
[26] Anthony, J. (2021). 70 SaaS Statistics You Must Learn: 2020/2021 Market Share & Data Analysis – Financesonline.com. Retrieved 6 December 2021, from https://financesonline.com/saas-statistics/
[28] Biswas, S. (2021). SaaS Market Statistics 2021. Retrieved 6 December 2021, from https://www.saasworthy.com/blog/saas-market-statistics-2021/
[31] Gould, R. (2021). The Most Important SaaS Statistics to Know in 2021. Retrieved 6 December 2021, from https://customerthink.com/the-most-important-saas-statistics-to-know-in-2021/