Table of Contents
Introduction and a Brief History
Nuclear reactors generate around 10% of the total electricity produced globally. Although nuclear fission is one of the most reliable and cheapest ways of producing of power, constructing a nuclear plant involves a lot of capital and technical expertise, which is why it’s still a difficult market to enter. There are 441 nuclear power reactors in operation around the world with a total net installed capacity of 393,542 MWe. Another 52 reactors that are still under construction would add 53,744 MWe to the global system.
The Obninsk Nuclear Power Plant (in the former USSR) was the first nuclear power station that produced electricity in 1954, while Calder Hall (UK, October 1956) became operational as the first full-scale power station solely devoted to producing electricity. A dramatic increase in fossil fuel prices and the energy crisis in the 1970s led to different countries embarking on civil nuclear energy programs. That’s the reason why most nuclear reactors were built between 1970-1985. By 2020, 13 countries were producing at least 25% of their total electricity from nuclear plants.
North America, Western Europe, Far East Asian countries and Central and Eastern Countries are currently the biggest producers of nuclear energy with the US, China and France leading the market. Let’s start with the basics of how nuclear energy is produced before moving onto the biggest producers by capacity.
The Basics of Nuclear Energy
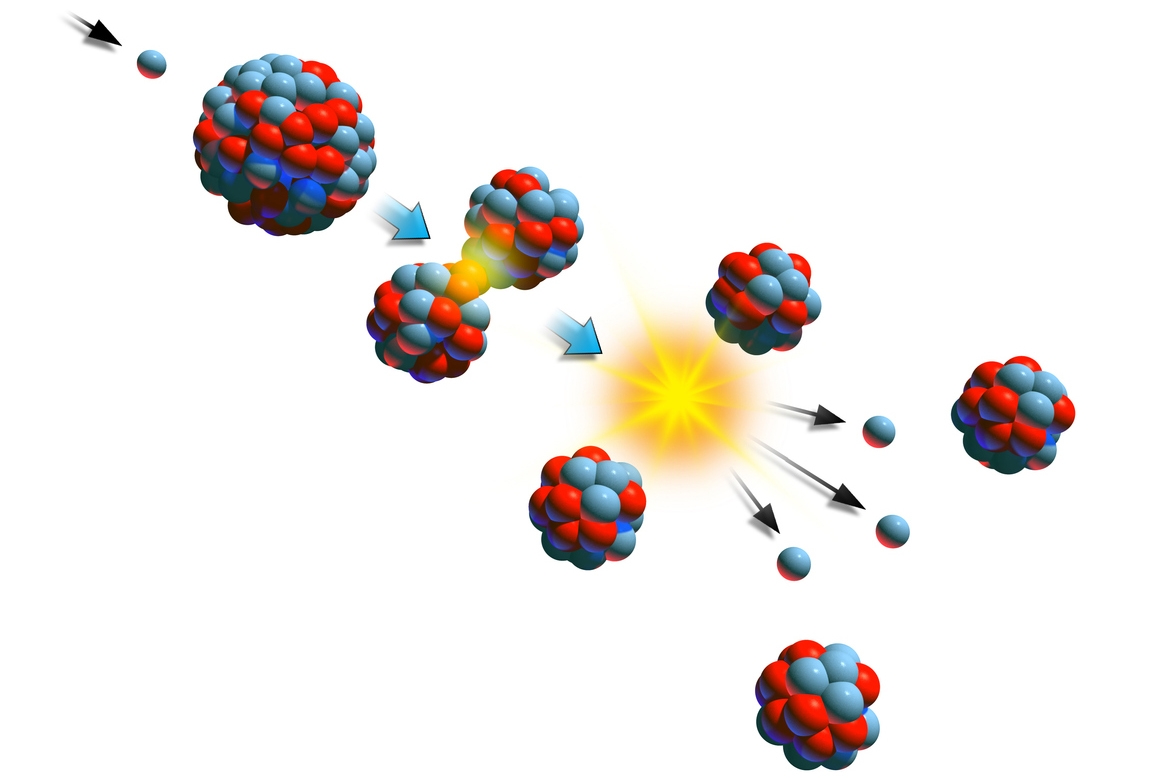
A nuclear reactor contains and controls nuclear reactions and is the heart of a nuclear power plant. Nuclear chain reactions produce heat, which is used to make steam that creates electricity by spinning a turbine. A nuclear reactor houses and controls nuclear fission, which refers to the process in which atoms are split to release huge amounts of energy. The core components of a nuclear fission reactor include:
- Nuclear Fuel (Uranium/Plutonium isotope)
- Moderator (Graphite core)
- Control rods (Change the speed of nuclear reaction)
- Coolant (used to boil water to run turbines)
- Concrete shield (to stop radioactive byproducts from getting out)
The technology used in nuclear reactors can vary from one country to another, but they all follow the same basic principles. For example, in the US, commercial nuclear reactions are light-water reactors i.e. normal water is used as a coolant as well as to moderate neutrons. Over 65% of these commercial reactors in the US are PWRs (Pressurized Water Reactors) in which water is pumped at very high pressure to prevent boiling. The rest of the reactors in the US are BWRs (Boiling Water Reactors), which refers to heating water and producing steam inside the reactor vessel.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Nuclear Power Generation
Advantages
Although nuclear energy is a cleaner and reliable alternative to fossil fuels, it’s also associated with some of the deadliest and dangerous weapons and nuclear disasters. Lengthy processes, very high costs and other barriers to entry means only a few countries can generate nuclear power. Different countries had different objectives and varying level of success with nuclear energy.
For example, France had massive success with its nuclear energy program as it wanted to break its dependence on foreign fossil fuels. It now produces almost 70% of its total electricity using nuclear plants. Not only France was able to break dependence on foreign fuel, it also succeeded in cutting down emissions. The key advantages and benefits of nuclear energy include:
- Nuclear energy is considered to be the cleanest of all the currently available energy resources
- No greenhouse gas emissions and does not contribute to global warming
- The cooling towers only emit water vapor (not toxic gases as many believe)
- No radioactive substances are released in the atmosphere
- Supports global decarbonization efforts
- Reduces dependence on fossil fuels and environmental effects related to mining and transportation
- Long lifetime of nuclear power stations
- Hi-tech research also benefits other industries
- Labelled as a green source of energy by the European Commission
However, despite being emission-free and clean, nuclear energy also has a hidden danger i.e. nuclear waste, which is highly radioactive. The bigger problem is that it can remain radioactive for a very long time (tens of thousands of years). Still, nuclear waste is considered to be a lesser issue to deal with than climate change because almost 90 percent of nuclear waste can be recycled. Producing nuclear energy is also a lot safer than producing electricity using fossil fuels as toxic chemicals released by burning fossil fuels are more dangerous for our health than nuclear waste.
Coal and oil are responsible for 1 out of 5 deaths globally. For reference, nearly 8.7 million people died because of burning fossil fuels, while only three accidents were recorded in the 70-year history of nuclear energy (Three Mile Island accident in 1979, Chernobyl disaster in 1986 and Fukushima nuclear disaster in 2011). Out of these three, only Chernobyl disaster caused deaths.
Other advantages of nuclear energy include:
- Nuclear energy has the highest capacity factor
- Less maintenance of plants
- Nuclear plants can operate for up to 2 years before refueling is needed
- Can produce max power >93 percent of the time
- Considered to be three time more reliable than solar and wind power plants
Disadvantages
One of the biggest reasons behind the opposition of nuclear energy is nuclear weapon proliferation. Conflicts like the recent Russia-Ukraine conflict can escalate and lead to use of nuclear weapons. The world has already seen the destructive power of nuclear weapons in WW2 in which the US atomic-bombed Hiroshima and Nagasaki. This not only led to immediate deaths of tens of thousands of innocent people, but also made life difficult in years to come.
Although the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons came into effect in 1970, there is always a risk of nuclear technology falling into wrong hands, especially in unstable countries where corruption is rampant. Disposing nuclear waste off properly is another challenge and although the chances of accidents are rare, radioactive nuclear waste remains extremely toxic.
Producing nuclear energy is cost-effective in the long run, but setting up a nuclear plant is the most time-consuming and expensive form of producing energy. Although cheap to run, building a nuclear plant can take decades, billions of dollars and highly skilled people.
- Disposing off nuclear waste is expensive and difficult
- Costs of building/decommissioning are high, require a lot of time
- Wastewater can cause thermal pollution locally, which can affect marine life
- Although rare, accidents can be catastrophic
- Negative public perception
- It’s difficult to react quickly to changes in the demand of electricity
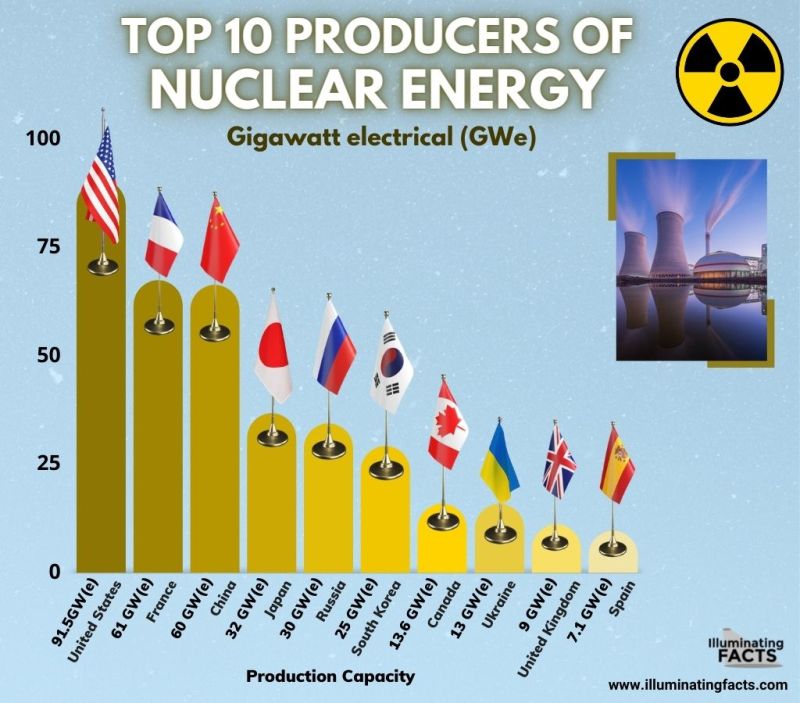
Top 10 Producers of Nuclear Energy (by Capacity, 2021)
1. United States
With a total generation capacity of 91.5 GW(e), the US generates the most nuclear energy in the world, which is roughly equal to 30 percent of global production. The US has massive energy demand and generates most of its electricity using gas and coal. That’s why its 93 nuclear reactors generate almost 20 percent of the total electricity despite having a tremendous generation capacity.
2. France
France generates around 70 percent of its electricity through nuclear plants, which by share is the largest in the world. Its 56 nuclear reactors generate more than 61 GW(e) and the country is on its way to build more nuclear reactors and entirely decarbonize electricity generation by 2050.
3. China
By 2026, China is expected to overtake the US in generating nuclear energy by adding more capacity to the existing 60 GW(E). China has massive energy requirements and its existing 60 GW(e) capacity only contributed 5 percent to the total demand (in 2019). With 51 operational nuclear plants and 18 under construction, China is well on its way to becoming world’s largest nuclear energy producer.
4. Japan
Japan used to be the number three producer until March 2011 and produced around 30 percent of its total electricity through nuclear plants. The Fukushima Daiichi plant melted down in 2011 following which all nuclear generation was paused for two years. Its 33 nuclear plants have a total capacity of 32 GW(e), while two nuclear plants are under construction and are expected to add 2.6 GW(e) to the national grid.
5. Russia
Russia produces around 30 GW(e) through its 38 nuclear plants. The former USSR was the pioneer of nuclear technology and is among the global leaders in modern nuclear technologies. Two reactors are under construction and will add another 2.3 GW(e) to the total capacity. In 2019, Russia produced approximately 20 percent of its total electricity through nuclear plants.
6. South Korea
South Korea’s 24 nuclear reactors have a capacity to produce 25 GW(e), which amounts to 25% of total generation. Four nuclear plants are under construction, which are expected to add 5.3 GW(e) to the total capacity.
7. Canada
Most of Canada’s 19 nuclear plants are located in Ontario and produce 13.6 GW(e), which roughly accounts for 15 percent of the total electricity generation. Canada’s nuclear plants feature CANDU (Canadian Deuterium-Uranium), which refers to using uranium as a fuel and pressurized heavy water as a moderator and coolant.
8. Ukraine
Ukraine produces a little over 13 GW(e) through its 15 nuclear plants, while two reactors are under construction and will add 2 GW(e) after completion. Its nuclear energy contributes to more than 50% of the total generation. However, it is highly dependent on Russia for nuclear fuel and technical assistance. That’s why Ukraine started purchasing fuel from the US to reduce its dependence amid geopolitical disputes.
9. United Kingdom
The UK produced 7% of its total electricity through its 13 nuclear plants (2019) and has a total capacity of 9 GW(e). Although two new reactors are under construction that will add 3.3 GW(e) to the system, by 2035 around half of UK’s reactors will retire, so the total generation is expected to decline in the future.
10. Spain
Although 7.1 GW(e) is not a big number compared to others in the top 10 list, Spain produces 22 percent of its total electricity through nuclear plants. All of Spain’s seven reactors were connected to the system between 1983-1988 and there has not been any significant development in this area since then. The Spanish government decided to eliminate nuclear power generation in 2018, terming it a ‘social decision’. Licenses for six out of seven reactors will expire in 2035, eventually putting an end to Spain’s nuclear energy program.
Conclusion
Nuclear energy has proven to be a reliable and emission-free source of energy. However, it’s still a controversial power source because of negative public perceptions. Constant anti-nuclear movements have led to the closure of nuclear plants in different countries, including Germany and Spain. On the other hand, countries like France are committed to producing emission-free power and many others are working to increase their nuclear energy generation capacity.
Contrary to negative perceptions, nuclear energy is still a lot safer and less hazardous than producing energy from conventional sources such as coal and oil. Nuclear energy super powers like the US, China and France have made good civilian use of what’s otherwise considered to be the deadliest of all technologies.
References
1. https://pris.iaea.org/pris/
2. https://www.dw.com/en/european-commission-declares-nuclear-and-gas-to-be-green/a-60614990
3. https://www.nytimes.com/2021/08/26/opinion/climate-change-nuclear.html
4. https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/c-change/news/fossil-fuel-air-pollution-responsible-for-1-in-5-deaths-worldwide/
5. https://www.energy.gov/ne/articles/nuclear-power-most-reliable-energy-source-and-its-not-even-close#:~:text=Nuclear%20Has%20The%20Highest%20Capacity%20Factor&text=This%20basically%20means%20nuclear%20power,than%20wind%20and%20solar%20plants
6. https://www.ans.org/news/article-510/globaldata-china-to-pass-us-nuclear-capacity-in-six-years/