HISTORY
Chinese foreign trade began as early as the Western Han dynasty (206 BCE-9 CE), when the famous “Silk Road” through Central Asia was pioneered by Chinese envoys. During later dynasties, Chinese ships traded throughout maritime Asia, reaching as far as the African coast, while caravans extended trade contacts in Central Asia and into the Middle East.
Foreign trade was never a major economic activity, however, and Chinese emperors considered the country to be entirely self-sufficient. During parts of the Ming (1368–1644) and Qing (1644–1911) dynasties, trade was officially discouraged. In the mid-eighteenth century, the government restricted sea trade by setting up the Canton System.
Beginning in the late 1970s, China reversed the Maoist economic development strategy and, by the early 1980s, had committed itself to a policy of being more open to the outside world and widening foreign economic relations and trade.
For thirty years following the establishment of the People’s Republic of China in 1949, there was virtually no trade between the two countries as Washington had severed ties with the communist government in Beijing. In 1979, the United States and China normalized relations, prompting an explosion of trade over the next four decades from a few billion dollars’ worth to hundreds of billions of dollars annually.
China also began a decades-long process of economic reform in the late 1970s under the leadership of Deng Xiaoping. His government loosened state control over the economy and allowed private industry to develop.
Chinese policymakers aimed to boost trade and investment, and in 1986 Beijing applied to rejoin the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade, the WTO’s predecessor. After protracted negotiations with the United States and other WTO members, China joined the WTO in December 2001. As a condition of admission, Beijing committed to a sweeping set of economic reforms, including steep tariff cuts for imported goods, protections for intellectual property (IP), and transparency around its laws and regulations.
At the time, U.S. President Bill Clinton and his advisors contended that bringing China into the global trading system would not only benefit the United States, but also foster economic and ultimately democratic reform in China. Still, the move was opposed by U.S. labor unions and many congressional Democrats, who argued that China’s weak worker and environmental protections would incentivize similar practices elsewhere and bring about a “race to the bottom.”
NEW DEVELOPMENTS
Today, the United States imports more from China than from any other country, and China is one of the largest export markets for U.S. goods and services. This trade has helped the United States in the form of lower prices for consumers and higher profits for corporations, but it has also come with costs.
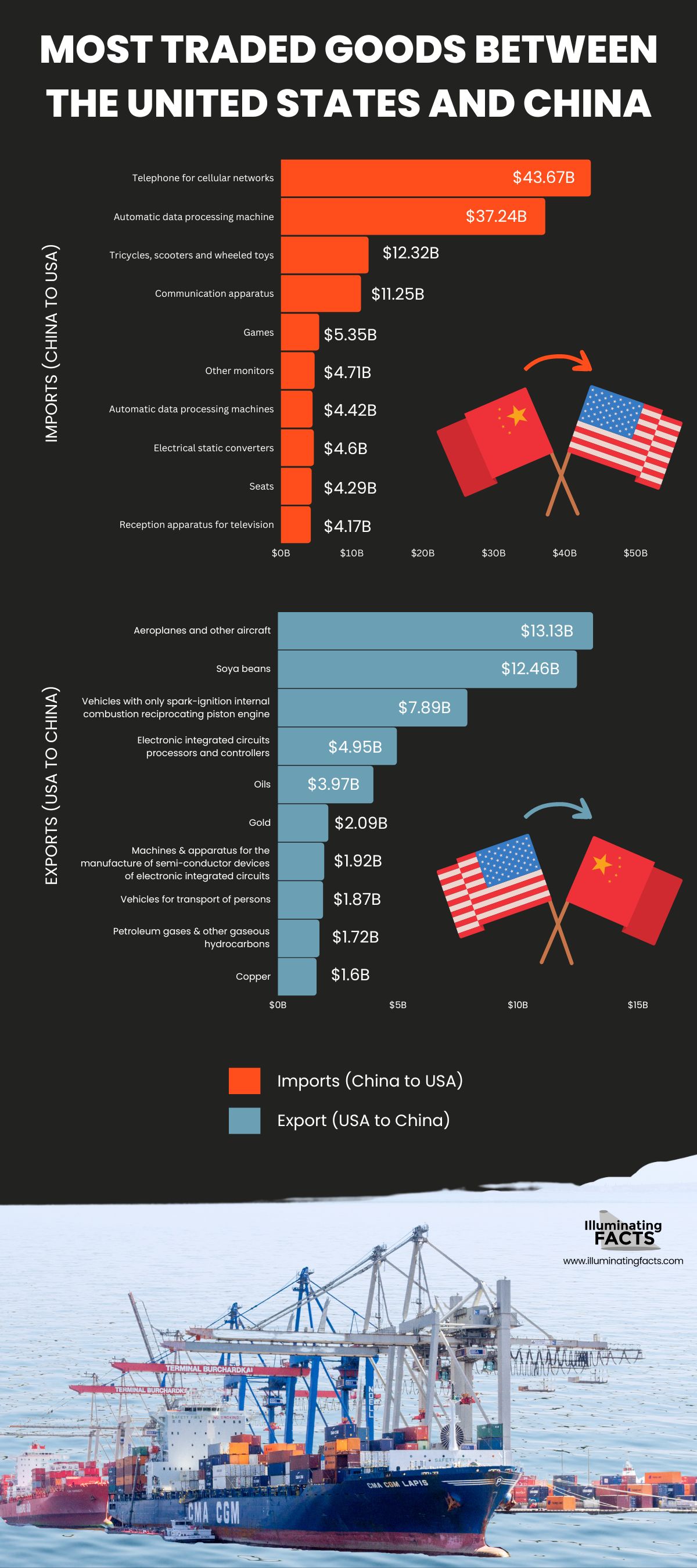
The Observatory of Economic Complexity on its 2017 report listed the ranking of the goods traded between the United States and China.
It can be noted that most of the traded goods between the two countries are almost in electronics, communication and transportation, transition elements are also included.
The US top imports from China include:
- Telephone for cellular networks or for other wireless networks at $ 43.67B
- Automatic data processing machines at $37.24B
- Tricycles, scooters and similar wheeled toys and other toys at $12.32B
- Communication apparatuses such as modem of an internet connections at $11.25B
- Games at $5.35B
- Computer Monitors at $4.71B
- Units of automatic data processing machines at $4.42B
- Electrical static converters at $4.6B
- Chairs (Seats) at $4.29B
- Reception apparatus for television $4.17B
China is best known for its electronics and technology-focused products with electronics products accounting for two-thirds of the top 10 Chinese imports. In 2017, China also dominated all electronics imports into the U.S., claiming over 60% of the market.
Meanwhile the US most traded goods to China include:
- Aeroplane and other aircraft at $13.13B
- Soya beans at $12.46B
- Vehicles with only spark-ignition internal combustion reciprocating piston engines at $7.89B
- Electronic integrated circuits; processors and controllers at $4.95B
- Crude Oil at $3.97B
- Gold at $2.09B
- Machines and apparatus for the manufacture of semi-conductor devices or of electronic integrated circuits at $1.92B
- Vehicles for transport of persons at $1.87B,
- Petroleum gases and other gaseous hydrocarbons at $1.72B
- Copper at $1.6B
A majority of these are highly specialized, manufactured products such as airplanes, integrated circuits, and semiconductors. The U.S. still relies on exporting many basic commodities such as gold, copper, and soya beans.
MOST TRADED GOODS BETWEEN THE UNITED STATES AND CHINA
IMPORTS (CHINA TO USA) | EXPORTS (USA TO CHINA) | ||
Telephone for cellular networks | $43.67B | Aeroplanes and other aircraft | $13.13B |
Automatic data processing machine | $37.24B | Soya beans | $12.46B |
Tricycles, scooters and wheeled toys | $12.32B | Vehicles with only spark-ignition internal combustion reciprocating piston engine | $7.89B |
Communication apparatus | $11.25B | Electronic integrated circuits processors and controllers | $4.95B |
Games | $5.35B | Oils | $3.97B |
Other monitors | $4.71B | Gold | $2.09B |
Automatic data processing machines | $4.42B | Machines & apparatus for the manufacture of semi-conductor devices of electronic integrated circuits | $1.92B |
Electrical static converters | $4.6B | Vehicles for transport of persons | $1.87B |
Seats | $4.29B | Petroleum gases & other gaseous hydrocarbons | $1.72B |
Reception apparatus for television | $4.17B | Copper | $1.6B |
In their 2020 report, the Observatory of Economic Complexity Bilateral Trade by Products, The United States exported $122B to China. The main products exported from United States to China were Soybeans ($13.9B), Integrated Circuits ($10.4B), and Crude Petroleum ($6.68B). During the last 25 years the exports of United States to China have increased at an annualized rate of 9.58%, from $12.4B in 1995 to $122B in 2020.
In the same year, China exported $438B to United States. The main products exported from China to United States were Computers ($48.9B), Broadcasting Equipment ($47.5B), and Other Cloth Articles ($16.1B). During the last 25 years the exports of China to United States have increased at an annualized rate of 10.5%, from $36.1B in 1995 to $438B in 2020.
In 2020, United States ranked 9 in the Economic Complexity Index (ECI 1.56), and 2 in total exports ($1.34T). That same year, China ranked 28 in the Economic Complexity Index (ECI 0.96), and 1 in total exports ($2.65T).
References:
https://www.cfr.org/backgrounder/contentious-us-china-trade-relationship#:~:text=Today%2C%20the%20United%20States%20imports,has%20also%20come%20with%20costs.
https://www.statista.com/topics/4698/sino-us-trading-relationship/#topicHeader__wrapper
https://oec.world/en/profile/bilateral-country/usa/partner/chn#bi-trade-products
https://oec.world/en