Table of Contents
Biggest Industry Players
It’s not that straightforward to categorically rate the biggest industry players. Some SaaS companies might not have huge numbers in their balance sheets, but it’s possible they are growing at a much higher rate than companies that have massive annual turnovers. Similarly, we also cannot judge SaaS companies only based on their client base or reputation.
On the other hand, it’s difficult to rate large companies such as Microsoft, IBM and Amazon because they are not just SaaS companies and also offer a wide range of other services, including PaaS, IaaS and storage services. To make things a little simpler, the list of ‘the biggest industry’ players’ focuses on SaaS-focused companies that specialize in delivering software over the internet. The list is primarily based on the market capitalization as of December 2021 (market cap= total value of company’s outstanding shares x market price per share).
Adobe ($266 Billion)
Adobe is well past the days of selling on-premises software and started moving to the cloud in 2007. The company replaced its Creative Suite (one-time license) to Creative Cloud Suite (subscription-based) in 2013. As a result, by 2017, subscriptions amounted for 86 percent of the total revenue, clearly indicating its future direction.
Its revenue has tripled since 2010 and the company has transformed into a subscription-based software behemoth. Adobe Creative Cloud, Adobe Experience Cloud and Adobe Document Cloud are some of the most popular and widely used products offered by Adobe.
Salesforce ($248 Billion)
Founded by a former Oracle executive, Salesforce started as a SaaS company right from the beginning in 1999 and was among the pioneers of cloud-based software. The company is famous for its CRM, but it also offers other enterprise and business solutions, including data analytics, market automation, app development tools and SMB-focused solutions. Company’s Customer 360 Suite empowers businesses to leverage data and make informed decisions, which ultimately leads to great customer experiences.
Oracle ($244 Billion)
Oracle is best known for its database management systems, but the company also offers a wide range of other solutions, including Enterprise Resource Management Systems (ERPs), Customer Relationship Management Systems (CRMs), Human Capital Management Systems (HCMs) and specialized hardware. It specializes in enterprise software, enabling enterprises to discover deep insights and see their data from a different perspective.
Intuit ($175 Billion)
The global tech platform specializes in financial management software and helps businesses identify patterns and provides them with actionable insights. Its product range includes QuickBooks, TurboTax, Mint, Credit Karma and MailChimp. Intuit offers solutions tailored for individuals, SMBs as well as enterprises, but its products are more focused on SMBs and the self-employed. The company boasts a customer base of over 100 million users, which shows its target market i.e. individuals and small businesses around the world.
Shopify ($173 Billion)
The Canada-based company serves over 1.7 million businesses in over 175 countries and runs around 1.6 billion e-commerce websites. That’s why it’s no surprise that the e-commerce platform is Canada’s biggest publicly traded company. Shopify makes it easier for small businesses to get started, run and grow their business and minimizes barriers to entry. Some key features of the platform include professional themes, branding and customization options, mobile compatibility, integrations including payment gateways, store management, marketing and order fulfillment.
SAP ($165 Billion)
Founded by former IBM employees in 1972, the Germany-based company was created aiming to to integrate real-time data processing and with business processes. It truly ventured into the cloud in 2011 by introducing SAP HANA, which is an in-memory database. SAP is now focused on machine learning, the Internet of Things (IoT), blockchain and complex analysis. According to SAP, around 77 percent of all global business transactions touch an SAP system and by 2025, revenue from its cloud business is expected to reach over €22 billion (from €8 billion in 2020).
ServiceNow ($125 Billion)
The workflow management platform enables businesses to efficiently manage their business processes and self-correct issues. Its serverless computing solutions cover five key business categories i.e. customer service, IT, security, business apps and HR. Digital workflows pave the way for hybrid workforce, allowing them for stay productive from anywhere. Company’s key products include IT Service Management, IT Operations Management, IT Business Management, DevOps, Security Operations and Operational Technology Management.
SnowFlake ($108 Billion)
SnowFlake is a data warehousing, data analytics and data storage provider that specializes in enabling critical workflows. It covers a wide range of industries, including financial services, technology, education and manufacturing. The company was recently founded in 2012 aiming to enable businesses to realize the true potential of their data. Its platform is compatible with other major platforms including Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud and Amazon Web Services. SnowFlake is only behind SAP Business Warehouse and has 11% market share in the data warehousing market.
Atlassian ($96 Billion)
Launched in 2001, the Australian tech company enables businesses to effectively manage projects and offers collaboration and software development solutions. Its product line includes Jira, Confluence, Bitbucket and Trello. Over 200,000 businesses rely on its collaboration and development tools to power innovation, automate manual tasks, collaborate and make smarter, data-driven business decisions.
Square ($78 Billion)
Square was launched in 2009 and offers merchant services for individuals, SMBs as well as enterprises and saves them from totally relying on cash registers. Its digital business solutions make it easier for clients to manage online stores, receive payments, manage inventory and manage other business processes such as paying salaries. In addition to payments, Square also offers PoS, developer platform, specialized hardware and other tools to help businesses and individuals succeed in a competitive market.
Autodesk ($61 Billion)
Autodesk was founded in 1982 and has been a market leader in CAD, 3D design, engineering and architectural applications. AutoCAD was released at a time when even mice didn’t exist and it was among a handful of software companies that made it possible to draw a perfect circle using a command. The company has been steadily moving away from perpetual licenses and announced discontinuation of selling perpetual licenses in 2016. Autodesk’s products are mainly used in construction, engineering, digital media and manufacturing.
Zoom ($60 Billion)
Zoom has become a household name, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic and has changed the course of remote work. It’s known for its video conferencing and chat services and is routinely ranked as the number one company by customers for meetings, conference calls and collaboration. The company was founded in 2011 by Eric Yuan, who previously worked as an engineer at CISCO. Zoom enables family members, employees, clients and almost anyone to collaborate in a better way. Some key enterprise clients of Zoom include ServiceNow, Veeva Systems and Atlassian.
Twilio ($50 Billion)
The cloud communications platform offers APIs for video, authentication, voice calls and SMS. It uses AWS (Amazon Web Services) as a host for its telephony infrastructure and is fully compliant with Secure Telephone Identity Revisited / Signature-based Handling of Asserted information using tokens (STIR/SHAKEN), which help protect against robocalls and spam calls. The company was founded in 2008 with an aim to revolutionize business communication by allowing businesses to integrate video, voice and messaging to web, mobile and desktop software.
Workday ($70 Billion)
Workday specializes in finance, HR and planning solutions and is focused to help managers manage business processes more efficiently. Compared to traditional ERP systems that usually have hard-coded features, Workday offers more flexibility and agility, and brings finance, HR, planning and data analytics under one roof. Its adaptive frameworks empower businesses to modify and configure their processes without having to code anything.
Veeva ($40 Billion)
Founded in 2007, the company specializes in cloud-based solutions for highly regulated industries, including life-sciences, pharmaceutical, consumer goods, cosmetics and chemicals. It offers different solutions that cover critical functions from research and development to commercial. Veeva aims to help businesses of various sizes to market their products faster while fully maintaining compliance. It offers a wide range of industry-specific solutions, including clinical, regulatory, quality, safety, medical and commercial solutions.
HubSpot ($31 Billion)
HubSpot specializes in cloud-based inbound marketing, sales and customer services solutions. Its CRM platform is designed keeping ease-of-use in mind and comes with the integrations and tools users need for managing content, marketing, sales and customer services. The CRM includes Marketing Hub, Sales Hub, Service Hub, CMS Hub and Operations Hub. The company is focused on ‘inbound’ and makes it easier for a business to work together as a whole. It supports over 900 integrations and allows users to create custom apps tailored to their unique requirements.
Cloudflare ($44 Billion)
Cloudflare provides security and performance optimization solutions to businesses around the globe. Its security solutions include API Shield, Bot Management, DDoS Protection, Page Shield, Rate Limiting, SSL/TLS Encryption for SaaS Providers and Web Application Firewall. Performance solutions include CDN, DNS, Load Balancing, Argo Smart Routing, Website Optimization Services and Video Stream Delivery. Cloudflare mitigated the largest recorded DDoS (Distributed Denial-of-service) attack ever in 2014 and another 2021, which is considered to be three times larger than previously recorded.
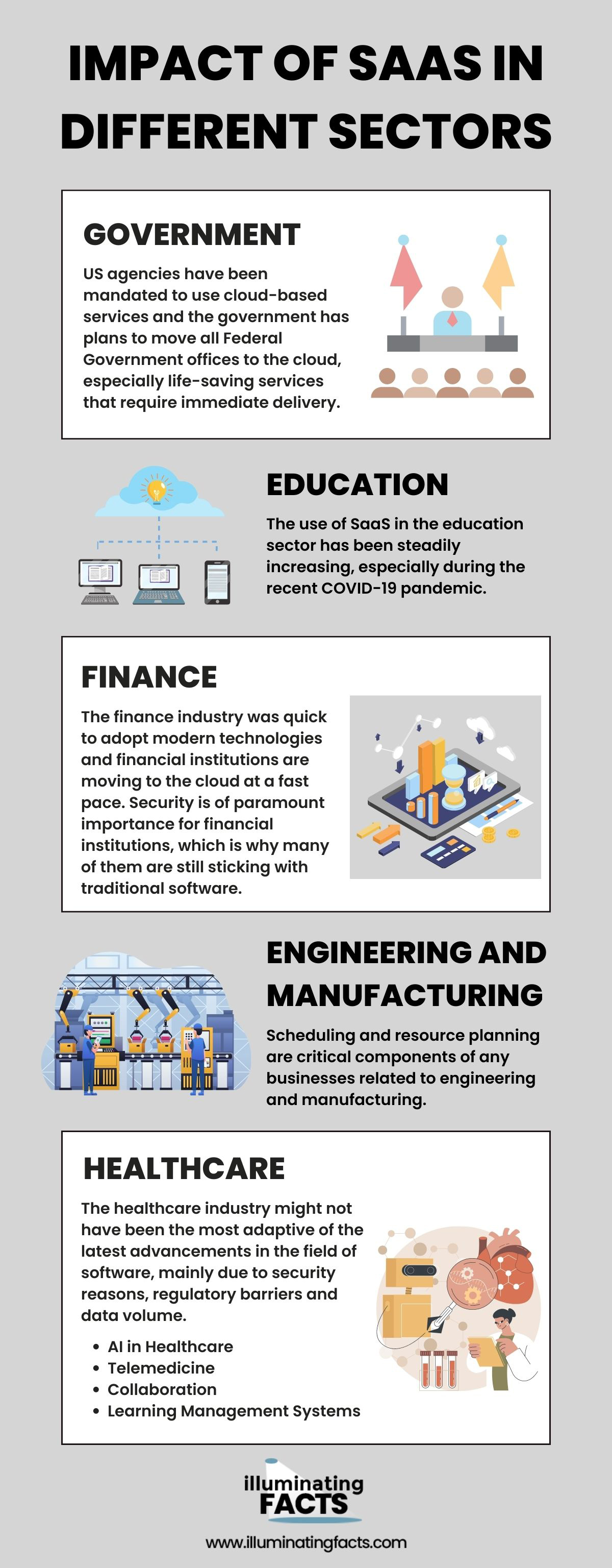
Impact of SaaS in Different Sectors
According to the “Cloud Adoption and Risk Report” published by McAfee [i], industry-specific SaaS platforms dominate the cloud services sector with government, engineering, finance, education and healthcare being the leading areas. The collaboration and file-sharing solutions had around 21 percent share in the category because these solutions are not industry-specific and anyone can use them. These solutions are followed by IT services (7.1%), cloud infrastructure (7.1%), development (6.5%), HR (6.3%), education (5.7%), Business Intelligence (5.3%), security (3.8%), media (3.6%) and healthcare (3.2%).
Government
US agencies have been mandated to use cloud-based services and the government has plans to move all Federal Government offices to the cloud, especially life-saving services that require immediate delivery. SaaS is fast becoming the standard for government agencies as governments try to modernize their operations and think of it as an enabler for their workflows. The main goal of using SaaS is to communicate effectively with the citizens, improve communities and as a result create thriving communities.
Managing a whole IT infrastructure and data centers is costly, cumbersome and time consuming for which SaaS is a natural remedy. The three biggest challenges government agencies face in digital transformation include aged/less skilled IT specialists, widespread use of legacy systems and keeping up with customer expectations.
They see SaaS as the right solution to these challenges and more than just a software delivery channel. SaaS makes it easier to adapt to change and accelerate organizational transformation. From hiring and retention to capital expense management and speedy delivery of services, SaaS helps government agencies to be prepared for current and unforeseen future challenges.
Education
The use of SaaS in the education sector has been steadily increasing, especially during the recent COVID-19 pandemic. SaaS solutions are easily accessible and offer scalability, mobility and interoperability. Compared to on-premises software, SaaS offerings align the interests of educational institutions and the vendor better. Anytime, anywhere learning, flexible budgeting, better customer services and uninterrupted access to information are some of the key reasons behind the adoption of SaaS.
The main advantages of using SaaS in the education sector include lower upfront costs, reduced IT complexity, predictable costs/ more accurate forecasting, immediate delivery of services, high scalability and integration capabilities, painless upgrades and ease of carrying out proof-of-concepts.
Finance
The finance industry was quick to adopt modern technologies and financial institutions are moving to the cloud at a fast pace. Security is of paramount importance for financial institutions, which is why many of them are still sticking with traditional software. However, SaaS products have evolved to be much more secure and reliable than they were a decade ago. In addition to ERPs, CRMs and HRMs, financial institutions are leveraging the flexibility and scalability SaaS offers to automate tasks, create collaborative work environments and maintain a high level of security.
SaaS provides fintech companies with higher agility to support volatile demand patterns and business cycles. Modern data analytics solutions provide them with a deep insight into their data and help them recognize otherwise hidden patterns. FinTech companies, especially banks simply cannot afford surprise interruptions because of what’s at stake. According to a recent survey [ii], finance leaders showed intent to protect their cyber security, customer experience and digital transformation programs as more people now perform online transactions than ever before.
New challenges require modern solutions, forcing financial institutions still using traditional software to keep up with modern technologies, minimize physical barriers and eliminate manual work and paper-based systems. Another report [iii] predicts that forecasting wont remain a monthly or quarterly exercise in the future and will be made on a real-time bases. Instant availability of information minimizes the limitations posed by traditional systems and allows businesses to discover real-time insights.
Engineering and Manufacturing
Scheduling and resource planning are critical components of any businesses related to engineering and manufacturing. Missteps can cost these businesses a lot and delay projects, ultimately resulting in dissatisfied customers. A growing number of contractors have either already moved to the cloud or are in the process of digital transformation. Cloud-based SaaS solutions help them avoid resource conflicts and gain a clear picture of resources, which ultimately results in better scheduling.
Another benefit of using SaaS solutions in the engineering industry is that these systems cut down waiting time usually spent on approvals, so things move faster. Dubbed as Industry 4.0, the field is undergoing a transformation by using solutions that combine advanced manufacturing with context-driven data for increased efficiency, seamless intercommunication and better operability.
Healthcare
The healthcare industry might not have been the most adaptive of the latest advancements in the field of software, mainly due to security reasons, regulatory barriers and data volume. But things have changed and a growing number of healthcare businesses are using cloud-based services to their advantage. From Electronic Medical Records (EMRs) to telehealth, R&D, and billing, SaaS is becoming more prevalent in the industry due to its benefits over on-premises software.
A research [iv] predicts the healthcare cloud computing market to generate $61 billion by 2025, which is an impressive CAGR (Compound Annual Growth Rate) of 18.7 percent (2019-2025). Many believe the industry has already reached a stage where cloud computing is about to dominate the whole industry.
AI in Healthcare
Although AI has many benefits including automation and pattern recognition, Artificial Intelligence in healthcare generally refers to the use of Machine Learning and deep learning tools to present, analyze and comprehend complex medical data. AI systems are getting better at approximating conclusions just based on the input data. The job of these AI systems is to gather data, process it and provide a well-defined output by recognizing patterns and creating logic.
The main benefits of using AI in healthcare include analyzing relationships between prevention/treatment techniques and outcomes, treatment protocol development, diagnosis, drug development, patient monitoring and personalized medicine. Robotics in the field of healthcare is believed to be the next big thing, which can transform surgeries and assist support health workers.
Telemedicine
Telemedicine market is on the rise, especially in the US and other developed countries and enables customers (patients) to receive medical care regardless of their physical location. It eliminates all physical barriers and provides equal access to healthcare. It saves patients from having to wait in queues and travel long distances to get medical attention.
Collaboration
Collaboration between medical professionals and departments require specialized tools. These tools save the medical staff from having to keep moving from one department to another for routine tasks such as collecting lab results and consulting with other professionals. Hospital Management Systems make it easier for doctors, nurses and other support staff to collaborate efficiently within the organization as well with experts around the globe.
Learning Management Systems
Medical professionals have to continuously learn new skills and acquire fresh knowledge throughout their career. Their busy schedules can be a great barrier to learning, which is eliminated by specialized SaaS tools that allow them to learn, prepare and take exams from anywhere.
Hardware as a Service
The SaaS industry has made a profound impact on the hardware sector by shifting burden from on-premises hardware to the cloud. Instead of purchasing, configuring and maintaining their own hardware, businesses can simply access their apps through a browser, which means fewer server closets to worry about. Although users still need a computer, laptop or a mobile device to access the app, all the heavy work is done by vendor’s machines.
Hardware as a Service (HaaS) refers to ‘renting’ hardware, which can be in combination with software, maintenance and installation and in which the user is not paying for the hardware itself. Hardware is an integral part of HeSaaS (Hardware enabled Software as a Service), which is like an evolution of SaaS that minimizes many challenges faced by businesses, especially startups.
For example, 3D Rendering, Computer Aided Design and GPU Compute require powerful GPUs and beefy computers. Instead of purchasing expensive systems, businesses have the option of creating projects on their own computer and rendering them on cloud-based systems offered by companies like Autodesk and Adobe. Migrating rendering and other heavy workloads to the cloud means businesses don’t have to keep spending large amounts of money on buying the latest hardware, especially GPUs.
Backup
Provision of backup, maintenance and upgrades by the vendor is one of the main selling points of SaaS solutions. Laws regarding data retention are complex and not all businesses can comply with them using in-house resources. Manually keeping track of data sync between local machines and the cloud can be a cumbersome task, especially when done multiple times a day.
Automated cloud backups save businesses from this hassle while ensuring compliance, security and data integrity. Backup as a Service is a sub-branch of SaaS that allows businesses to store sensitive information locally and move other large amounts of data to the cloud.
Conclusion
The impressive growth rate of the SaaS industry in the past and projected growth in the future clearly shows where we are heading into the future. With Artificial Intelligence, the Internet of Things and Machine Learning becoming more mature, the momentum indicates SaaS will play an even bigger role for businesses as well as home users. Private capital and venture firms have played a pivotal role in advancement of the industry and big SaaS players are expected to achieve sustained growth in the foreseeable future.
[i] “Cloud Adoption and Risk Report”. Retrieved form https://www.mcafee.com/enterprise/en-us/assets/skyhigh/white-papers/cloud-adoption-risk-report-2019.pdf
[ii] “PwC US CFO Pulse Survey”. Retrieved from https://www.pwc.com/us/covid-19-survey
[iii] “Finance 2025: Digital transformation in finance”. Retrieved from https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/pages/finance-transformation/articles/finance-digital-transformation-for-cfos.html
[iv] “Healthcare Cloud Computing Market – Global Industry Analysis”. Retrieved from https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/sample/healthcare-cloud-computing-market