As the world’s population is growing, the demand for energy has also multiplied. Yet, given the growing concerns around fossil fuels, homeowners worldwide are actively seeking alternative ways to power their residences and businesses. This is where the concept of renewable energy comes into play.
Renewable energy encompasses power sourced from naturally replenished resources. This concept has gained popularity in recent years because of its potential advantages. It is a great way for homeowners to save on energy bills while also doing their part to help the environment.
But what exactly is renewable energy? How did it emerge? And what possibilities exist for homeowners today who are looking to reap the benefits of renewable energy sources? This post will explore each of these questions in detail.
What is Renewable Energy
Renewable energy, as defined by the U.S. Department of Energy, is “energy produced from sources like the sun and wind that are naturally replenished and do not run out.” [1] These sources can be anything from water power (hydropower), sunlight (solar power), or wind power (wind turbines).
The key distinction here is that these sources are self-replenishing. Once they have been used, they will naturally regenerate over time, allowing them to be used again and again without any impact on the environment.
Renewable vs Traditional Energy
| Factor | Renewable Energy Sources | Traditional Energy Sources |
| Environmental Impact | Low greenhouse gas emissions and minimal air and water pollution. | High emissions of pollutants and greenhouse gases, contributing to climate change and health issues. |
| Resource Availability | Abundant and virtually inexhaustible, reliant on natural processes. | Finite resources like coal, oil, and natural gas, subject to depletion. |
| Fuel Source | Derived from natural elements like sunlight, wind, water, and Earth’s heat. | Extracted from fossil fuels, resulting in resource extraction and environmental degradation. |
| Energy Independence | Enhances self-sufficiency by generating power on-site or from local sources. | Often reliant on imports of fossil fuels, potentially affecting energy security. |
| Operating Costs | Generally lower, as renewable systems have minimal fuel and maintenance costs. | Operating costs can be high due to fuel extraction, transportation, and emissions management. |
| Technological Advancements | Rapid advancements drive efficiency improvements and cost reductions. | Advancements can occur, but many existing technologies are mature. |
| Environmental Regulations | Generally, align with clean energy goals and receive policy support. | Regulations aim to reduce pollution but may not entirely mitigate environmental impact. |
| Energy Transition Challenges | Requires infrastructure upgrades and may face intermittent energy supply. | Established infrastructure can resist change due to vested interests and inertia. |
The Genesis of Renewable Energy: A Historical Perspective
The use of renewable energy by humans can be traced back to thousands of years ago. The Roman Empire and eastern Mediterranean region extensively used water power by at least the first century BCE. [2] Similarly, the ancient Greeks harnessed the power of wind to propel their sailing ships and aid navigation. [3] Although the boat technology and innovation has come very far, these ingenious uses were just a precursor to what would come about in later centuries.
The Industrial Revolution: A Double-Edged Sword
The industrial revolution saw a massive increase in human progress both scientifically and technologically. But, it also had its drawbacks environmentally as traditional sources, such as coal, were burned at unprecedented rates with little regard for their environmental impacts. [4] The dawning realization that these resources would eventually be depleted led to the development of alternative forms of energy. The most prominent example of this are hydropower plants which utilize water turbines to generate electricity from moving rivers and oceans.
The Oil Crisis: A Wake-Up Call for Renewable Alternatives
The oil crisis in 1973 was a wake-up call to many countries that their dependence on finite fossil fuels needed to be addressed or else they risked running out altogether. [5] Since oil is one of the largest energy sources, its shortage led to a surge in research into renewable technologies such as solar panels, wind turbines, and geothermal plants. All of these had the potential to generate a considerable amount of electricity without harming the environment or depleting any resources in the process.
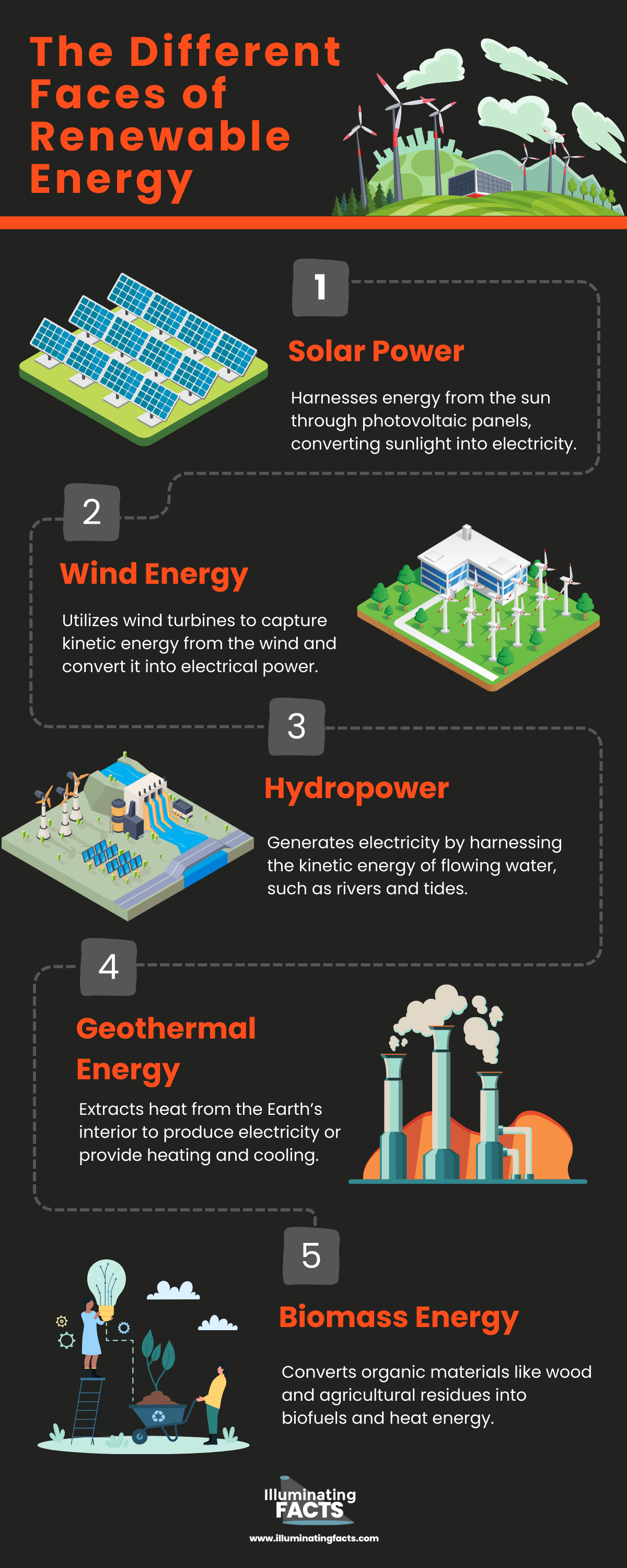
The Different Faces of Renewable Energy
| Renewable Source | Description |
| Solar Power | Harnesses energy from the sun through photovoltaic panels, converting sunlight into electricity. |
| Wind Energy | Utilizes wind turbines to capture kinetic energy from the wind and convert it into electrical power. |
| Hydropower | Generates electricity by harnessing the kinetic energy of flowing water, such as rivers and tides. |
| Geothermal Energy | Extracts heat from the Earth’s interior to produce electricity or provide heating and cooling. |
| Biomass Energy | Converts organic materials like wood and agricultural residues into biofuels and heat energy. |
There are many types of renewable energy available for homeowners today. And, all offer viable options for sustainable living and reducing your reliance on traditional sources of energy.
Solar Power
Solar power is one of the most well-known forms of renewable energy. Solar panels absorb the sun’s energy and convert it into electricity which can be used by your home. This is a great way to reduce your reliance on traditional sources of electricity and build a more sustainable home.
This form of renewable energy is especially useful in areas with plenty of sunshine. However, it isn’t limited to this type of location alone. With the help of modern technology, solar power can be used even in cloudy and partially sunny areas.
Wind Power
Wind power is another type of renewable energy that homeowners can use to power their homes. Wind turbines generate electricity by harnessing the kinetic energy of wind.
Thanks to advances in technology, wind turbines are now more efficient than ever before. Building a small wind turbine in your backyard is a great way to reduce your electricity bill and contribute to a more sustainable lifestyle.
Hydro Power
Hydro power is one of the oldest forms of renewable energy and utilizes the force of water to create electricity. Hydroelectric dams use the falling water from rivers or streams to turn turbines and generate electricity. Homeowners can also build small-scale hydroelectric systems that generate electricity from smaller bodies of water such as streams or even backyard ponds.
Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy takes advantage of the heat stored by Earth’s core by tapping into hot springs or drilling deep underground wells. The heat is converted into electricity using specialized heat pumps that transfer heat from one place to another.
This form of renewable energy can be used to heat buildings or generate electricity. Hence it is a viable option for homeowners looking for an alternative source of energy.
Biomass Energy
Biomass energy is produced by burning organic materials such as wood, agricultural waste, and algae. This form of renewable energy produces less carbon dioxide than traditional sources of fuel and can be used to generate heat and electricity for your home. Biomass is also renewable and can be sustainably harvested in order to maintain a steady supply.
The Science Behind Renewable Energy
Renewable energy sources come in many forms, and learning how to harness these energies can help reduce your personal environmental footprint. In this section, we explore the science behind the most common renewable energy sources available to the modern homeowner.
Photovoltaic (PV) Cells: How Solar Panels Work
Photovoltaic cells utilize light energy from the sun to generate electricity. They are made up of semiconductors, such as silicon, often arranged in layers inside solar panels to maximize efficiency.
When sunlight comes into contact with the cell’s surface, its electrons become energized and start flowing freely, creating an electrical current. Essentially, these semiconductors absorb sunlight and convert it into electricity, which is then stored in a battery. This current then passes through an inverter, which converts it into usable electricity for powering appliances within a home.
Wind Turbines: The Mechanics of Wind Energy
Wind turbines harness the power of wind to produce electricity. As air passes over a turbine’s blades, they begin to spin in a circle. This circular motion turns a generator that produces electricity.
Essentially, wind turbines operate like miniature windmills, the more air that passes through the turbine, the more energy it generates. They are typically installed in areas with strong winds, such as near mountains or on hilltops, to maximize their potential output.
Hydroelectric Dams: The Physics of Water Power
Hydroelectric dams use water power to generate electricity. A water turbine is placed at the bottom of a dam, and when water flows through it, the turbine spins around creating electrical energy. This energy is then transported via cables and converted into usable household electricity with the help of an inverter.
This is a reliable source of renewable energy that can provide power for entire communities.
Geothermal Wells: The Earth as a Heat Source
Geothermal wells use natural heat from the Earth’s core to produce electricity. A geothermal system consists of several wells drilled deep into the Earth’s crust (about 2 to 4 miles deep) which tap into underground reservoirs of hot steam or liquid water. This hot steam or liquid water is pumped up through pipes and sent to an above-ground turbine. The pumped hot air and steam spin it around to generate electricity.
These systems can provide a stable source of renewable energy for homes or small businesses located near naturally occurring underground hot springs or volcanoes.
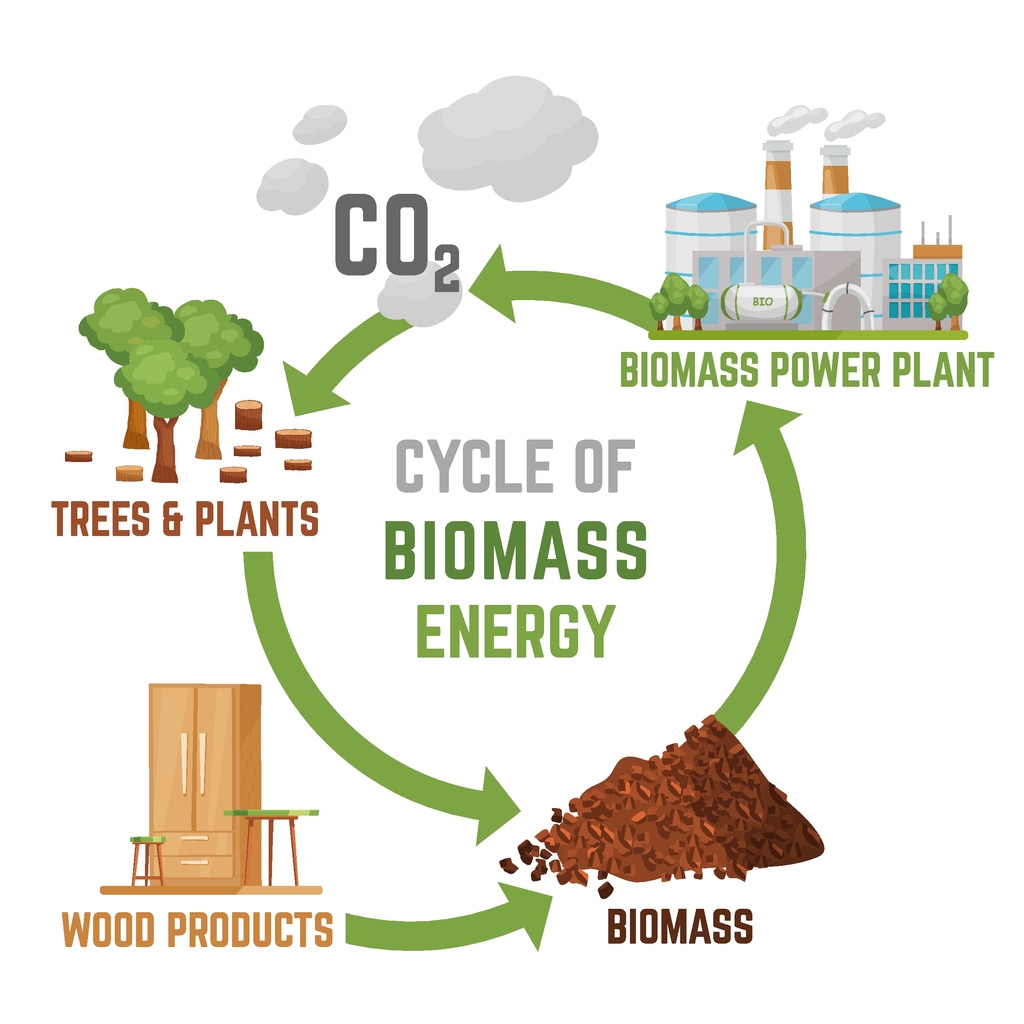
Biomass Conversion: From Waste to Energy
Biomass conversion is a process whereby organic materials, such as food waste, are transformed into usable energy through burning or fermentation. In biomass conversion systems, organic waste materials are heated and combined with air and steam, creating a combustible gas, known as biogas, which is then used as fuel for a generator, resulting in electricity production.
These conversion systems offer homeowners an alternate way to reduce waste and generate clean energy at the same time.
Technological Advancements: The Future is Now
The future of renewable energy has never looked brighter. Homeowners can now access renewable energy at prices that are competitive with traditional sources of energy. With decreasing costs in solar photovoltaic (PV) technologies, installing a solar array on your home or business is no longer out of reach. The advances in microinverters and string inverters have also enabled homeowners to monitor and manage their solar output more efficiently.
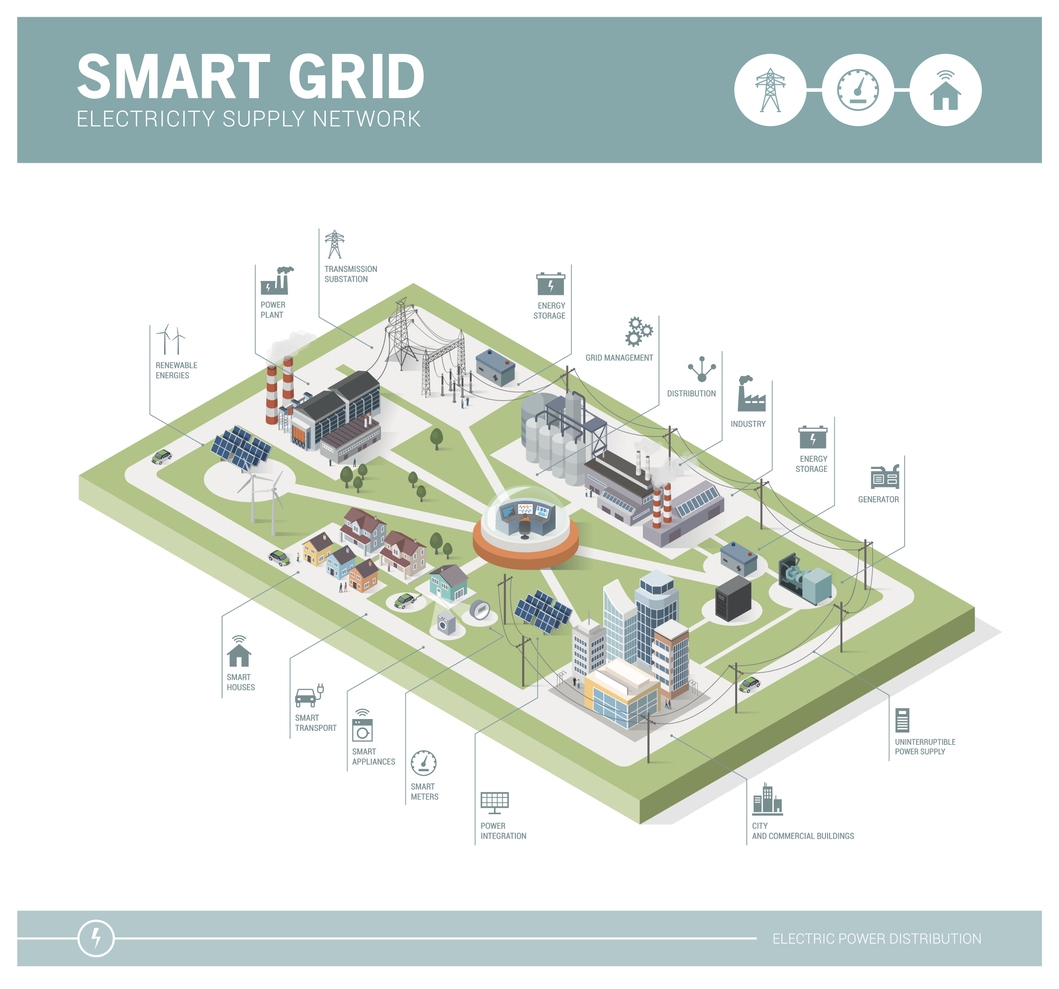
Smart Grids: The Internet of Energy
As more homes become connected to the grid through smart grids or microgrids, the possibilities for renewable energy become even more plentiful. Smart grids allow homeowners to receive data about their usage and take control of their power consumption. This technology also encourages distributed generation which enables the homeowner to generate clean electricity directly from their own home without having to rely on the grid.
Battery Technology: Storing the Sun and Wind
The rise in battery technology has also been instrumental in enabling homeowners to take advantage of renewable energy sources. Batteries enable homeowners to store excess energy produced by their solar panels or wind turbines. This way they can access electricity even when the sun isn’t shining or the wind isn’t blowing.
Powerful batteries capable of storing up to 10 kWhs of energy are readily available on the market. A single one of these is enough to power a typical household for several days or even weeks depending on use.
Conclusion
With individuals and businesses becoming more mindful of the need to reduce their environmental footprint, renewable energy is an increasingly attractive option for many homeowners. The advances in technology over the past decade have enabled homeowners around the world to access renewable energy sources that were once only available to large-scale businesses and industries. As solar and other renewables become more affordable and efficient, a good number of the population is making the switch from fossil fuels to these clean energy sources.
References
- Renewable energy. (n.d.). Energy.gov. https://www.energy.gov/eere/renewable-energy
- Hydro power in ancient times: Ca. 300 BCE–500 CE – Electricity & alternative energy – Alberta’s energy heritage. (n.d.). Historic sites, museums and archives | Alberta.ca. https://www.history.alberta.ca/energyheritage/energy/hydro-power/hydro-power-in-ancient-times.aspx
- A brief history of sailing in Greece – Part 1. (2018, November 22). Yacht Charter Croatia – All Charter Yachts in Croatia. https://www.yacht-rent.com/greece/brief-history-of-sailing-in-greece-part-1
- What was the Industrial Revolution’s environmental impact? (n.d.). Greenly: The go-to carbon accounting platform for your business. https://greenly.earth/en-us/blog/ecology-news/what-was-the-industrial-revolutions-environmental-impact
- From oil crisis to energy revolution – how nations once before planned to kick the oil habit. (n.d.). Rapid Transition Alliance. https://rapidtransition.org/stories/from-oil-crisis-to-energy-revolution-how-nations-once-before-planned-to-kick-the-oil-habit/