Background
Outer space, often called space, is made up of relatively empty regions of the universe outside the atmospheres of celestial bodies. The word “outer” is used to distinguish it from airspace and terrestrial locations. Since the density of the atmosphere steadily decreases as altitude increases, there is no distinct barrier between the atmosphere of Earth and space. [1]
Space is almost completely devoid of matter, has very low pressure, and is virtually a perfect vacuum. Due to the lack of molecules positioned close enough to one another, sound cannot travel over space. In the “emptier” but not quite empty regions of the universe, bits of gas, dust, and other matter float, whereas, in the denser regions, planets, stars, and galaxies can be discovered. Additionally, no one is quite certain of the size of space, and astronomers are not certain if our cosmos is the only one that exists. This implies that space may be far larger than we realize. [2]

an abstract space illustration

the Sun producing massive radiation bursts

a full moon

a black hole
All of these are facts about space, and there are more interesting facts about outer space that we can learn. However, there is also certain information that may seem to be facts but are actually not true about space. That is why it is very important to be careful when getting information, especially if you intend to pass your knowledge to other people.
There are a lot of myths about space that have been circulating for many years now. Some have been debunked for a long time, but many still continue to believe in them. Therefore, to help stop the spread of misinformation, we’ve gathered in this post the myths about space that many people think are actual facts, along with the truths behind them.
Myth#1: We explode in space.
In space, humans don’t explode. Our tissue is strong enough to withstand the imbalance even though outer space implies a lack of air pressure, which typically balances the internal pressure in our bodies. The blood arteries can tolerate the internal pressure without blowing up, according to Richard Harding’s book “Survival in Space.”
In the absence of a space suit, humans do die in space. But they die for the same cause that humans who are submerged for an extended period of time do: oxygen deprivation. According to the Federal Aviation Administration, humans remain fully conscious for 9 to 12 seconds after being exposed to a vacuum. The spacesuits also provide protection from other hazardous elements like radiation and ice. However, these do not immediately result in demise and most definitely do not trigger an explosion. [3]
Myth #2: The Sun is a ball of fire.
The Sun may be hot, around 27 million degrees Fahrenheit at its core, but it is not a massive open flame like many people believe in. The Sun doesn’t “burn” in the sense that we associate with burning paper or logs in a fire. Because the Sun is a massive ball of gas and nuclear fusion is occurring at its center, the Sun shines.
Actually, it produces heat and light through a process known as nuclear fusion, in which hydrogen atoms collide to produce helium. The neighboring materials (other protons, electrons, etc.) are then heated by this energy. This heating eventually leaves the star’s surface and radiates out into space as the heat and light that we know stars release. It first begins in the star’s core. [4] [5]
Myth #3: There is sound in space.
At least not in the way we perceive it on Earth, but sound doesn’t exist in space. This is due to the fact that sound travels by the vibration of particles, whereas space is a vacuum. There are air molecules that vibrate on Earth that carry sound to your ears, but in nearly empty areas of space, there are no (or very, very few) particles to vibrate. Hence there is no sound.
The longitudinal wave that makes up sound moves in the medium through which it is traveling, causing back-and-forth oscillation of the particles. The speed of sound varies from substance to substance and is most quickly transmitted through solids, liquids, and gasses. It travels through a medium at this speed. We are lucky because if there is sound in space, the sound of the Sun would be audible to us on Earth at an astonishing 100 dB, which would be like listening to a rock concert nonstop. [6]
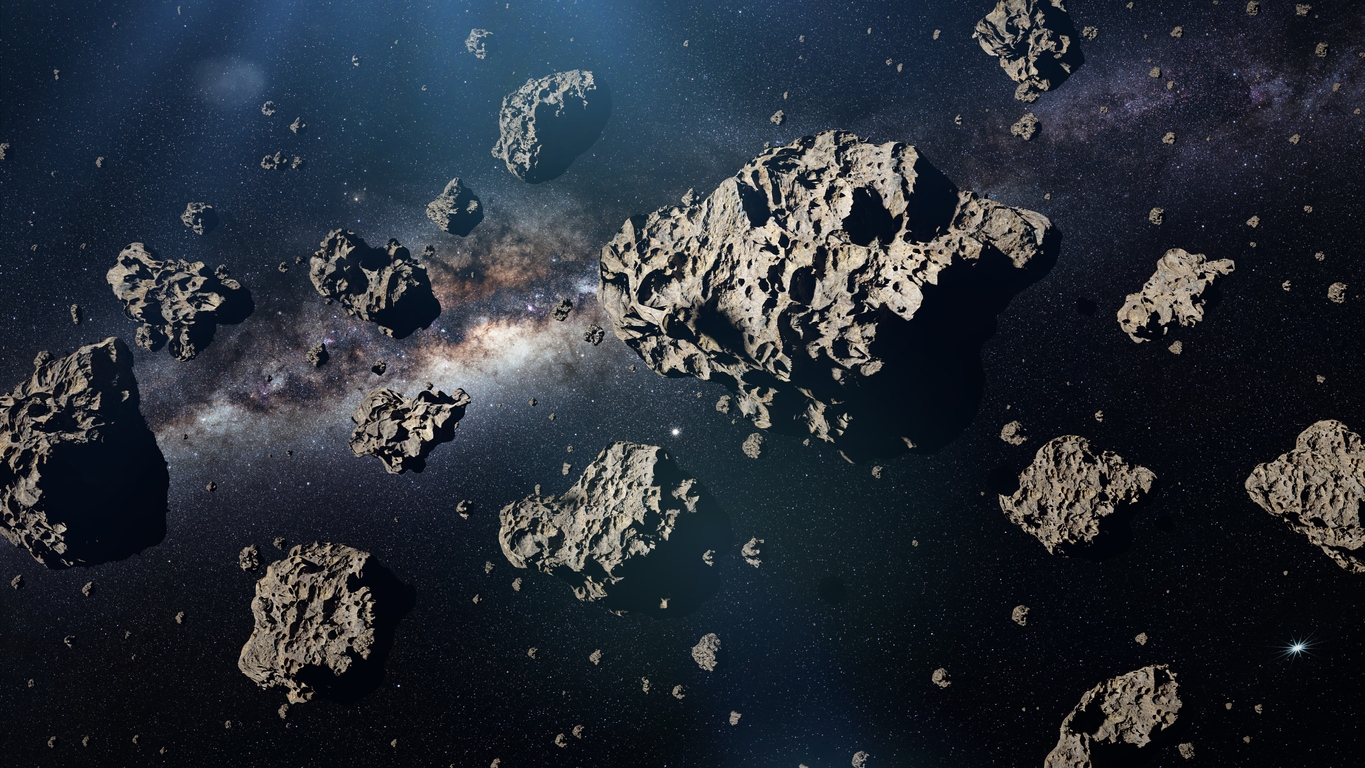
Myth #4: You can’t travel through an asteroid belt.
A lot of people believe that the asteroid belt is made up of tons of giant asteroids, making it dangerous to pass through. However, that is not true. In reality, the asteroid belt is made up of tons of pebble-sized asteroids and a few giants, such as Pallas, Ceres, Hygiea, and Vesta, which are more than 250 miles in diameter.
Therefore, contrary to popular belief, it is much simpler to pass through the belt in actuality. And hitting an asteroid has the same likelihood of happening as discovering a pot of gold. This has also been proven with the 11 probes sent through the belt without a single accident. [7]
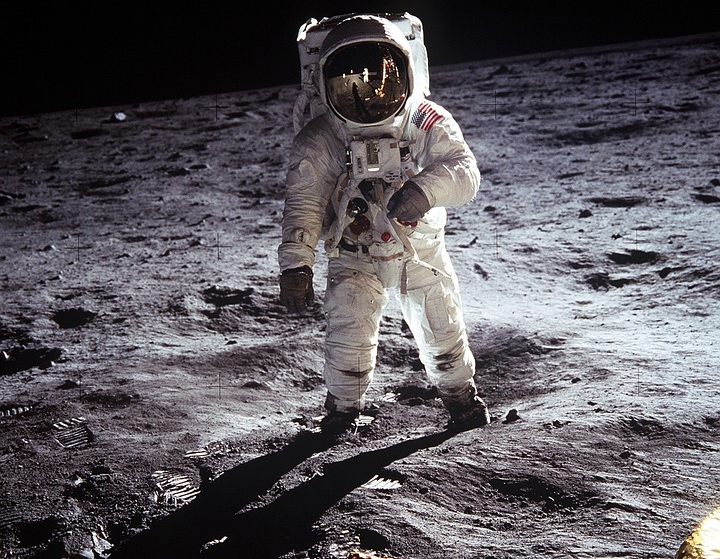
Myth #5: The Apollo moon landings were fake.
According to conspiracy theories, the Moon landings were faked, Apollo 11 did not happen, and humans never set foot on the Moon. Even though there has been lots of information out there that debunked these theories, the myth still lives on. That’s why we are going to explain them here again.
The first conspiracy theory is that there are no stars in the pictures of the NASA moon landings. A lot of people believe that if the image really was taken on the Moon, the sky should be filled with stars. But the truth is that both the astronauts and the lunar landscape are brightly lit by the Sun. Even though it may appear that the sky is black, keep in mind that it is, in fact, daytime on the Moon when the photos are taken. If you want to capture a photo of a scene with strong lighting, your camera’s shutter speed must be quick, and its aperture must be very narrow. Stars and other dim objects won’t be visible in the situation. [8]
The next conspiracy theory is that the Apollo 11 US flag is waving in the wind, but there is no airstream on the Moon. There is really no wind on the Moon, and the flag is not waving. To enable it to fly honorably, a telescoping pole has been extended along the top of the flag. Since it had been set up like that, it appeared to be waving in the wind. [8]
Lastly, why are there no marks from the lunar modules that landed there, but there were footprints? The answer to this is simple. The lunar modules did not leave marks on the surface in some places as their mass was evenly spread than the astronauts’ weight in their boots.
Myth #6: Going into space makes you weightless.
The majority of scientists concur that space begins 62 miles above the Earth’s surface when the atmosphere is essentially a vacuum. But after you pass this point, you don’t suddenly become weightless. You would experience gravity many times stronger than on Earth if you were in an accelerating rocket. You’d only feel weightless when you start falling.
To orbit something is to continually descend around it. The solar system around the Milky Way, the moon around Earth, and the Earth around the sun are all tumbling toward one another in a wild cosmic dance. If you were 250 miles above the surface of the Earth, you would have to circle the globe at 17,500 mph, which is the same speed as the International Space Station and its occupants, in order to experience continuous free fall. [9]
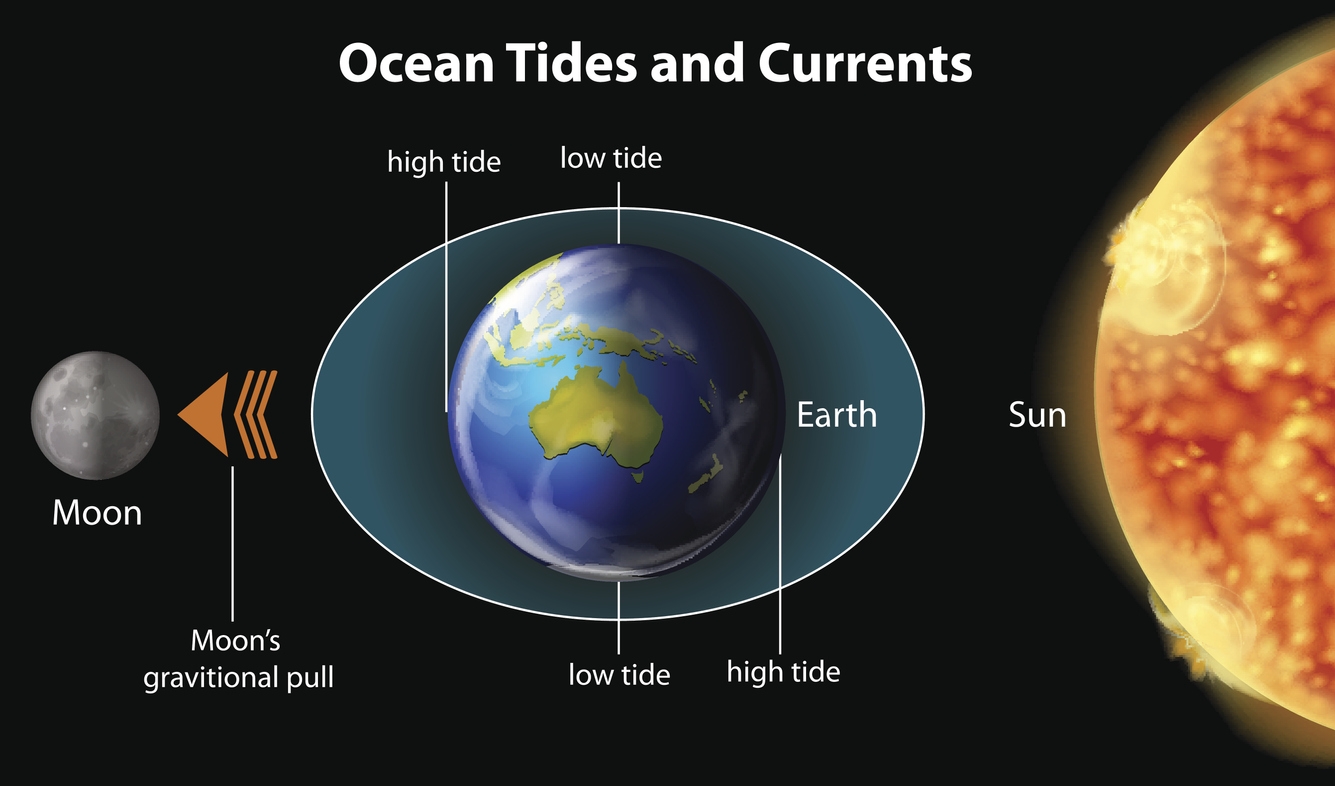
Myth #7: The moon’s gravity pulling on water causes the tides.
This is only a bit true because the science behind the ocean tides of the Earth is anything but straightforward. The moon indeed affects ocean water. However, the amount of that force at any given time is only a small fraction of the gravity of the Earth. What causes the tides are, in reality, the interplay of gravity among the Earth, the moon, and the Sun, which creates a tidal force. Also, it is more of a squeeze than a pull.
The moon’s gravity pulls on every molecule of water. However, that gravitational acceleration is insignificant on its own. But because ocean water unites as one liquid body and spans around 71% of Earth’s surface, all of those minor pressures add up to generate a large pressure that is known as the tidal force. [9]
Near the poles, Earth’s gravity pulls water molecules mostly straight down. The largest force toward the moon is felt by those on the face of Earth closest to it, while the smallest acceleration is felt by those on the other side of the planet.
Together, these interactions create pressure on the ocean that typically pushes the water toward the equator and away from the poles, where it is barely powerful enough to defy gravity and form two bulges known as the high tides. Tides track the moon as it revolves around the Earth every 28 days, but it’s not quite that straightforward. The curvature of the seafloor, the location of the coasts, and the Coriolis effect (produced by Earth’s rotation) all influence where and to what extent tides occur, resulting in a complex pattern of “tidal nodes” as the water sloshes around, just as it does inside an aquarium.
The tides are also influenced by the gravity of the sun, which is responsible for around one-third of the phenomena. Neap tides are smaller than usual when the sun and moon are aligned, whereas spring tides are bigger when the sun and moon are not aligned. Also, because there isn’t enough water in smaller bodies of water like lakes and pools to generate a pressure that can clearly overcome Earth’s gravity, tides aren’t visible in these smaller bodies of water. [9]
Myth #8: The vacuum of space is always cold.
The vacuum of space can reach temperatures as low as -454 degrees Fahrenheit when you’re in complete darkness at the coldest location in the known universe. However, temperatures can suddenly rise to a scorching 250 degrees Fahrenheit in sunlight close to Earth. The reflective white space suits that astronauts wear are for this reason. [9] Therefore, it is not true that the vacuum of space is always cold.
Myth #9: Black holes are like vacuums.
Most of the time, black holes are seen by people as something evil. But in fact, they are fascinating objects in space. Many also believe that black holes are like vacuums that suck everything in. Black holes aren’t necessarily out there “sucking” everything up in the universe just because they can have a strong gravitational attraction on objects passing by. [10]
Black holes aren’t the giant cosmic devourers we make them out to be, despite the fact that they do have event boundaries and that anything that crosses one can never escape. They are instead the messiest eaters you can imagine. Instead of thinking about vacuums, it is better to think of them as cosmic Cookie Monsters. [11] Black holes are largely dormant until a star comes too close and awakens them from their slumber. They don’t suck up everything around them; instead, they stay largely stationary. However, the black hole merely breaks apart a small portion of the nearby objects.
Myth #10: A light-year measures time.
When the term “light-year” is discussed, many of us would think about time. But the truth is that a light-year does not measure time, but it instead measures distance. According to NASA, a light-year is the total distance that a beam of light moving in a straight line travels in a year. Since light travels at around 300,000 kilometers per second, a light-year is around 10 trillion kilometers or 6.2 trillion miles. [12]
Myth #11: Your blood would boil in space.
Many people believe that their blood would boil in outer space, but this isn’t exactly true. There is what we call the Armstrong limit or Armstrong’s line. It pertains to the atmospheric pressure created by the altitude, which causes water to boil at the body’s typical temperature of 37 °C (98.6 °F). At the height of roughly 18 km (60,000 ft) to 19 km, the Armstrong line starts (62,000 ft). Above that altitude, it would be safer to wear a spacesuit for your own protection. However, your blood won’t boil, as the walls of your veins keep your blood pressure high enough to prevent boiling. [13]
At or above the Armstrong limit, exposed bodily fluids such as saliva, tears, urine, blood, and the liquids wetting the alveoli in the lungs will boil away in the absence of a pressure suit, and no amount of breathable oxygen delivered by any means will keep a person alive for more than a few minutes. However, vascular blood, or the blood within the circulatory system, will not be affected. [13]
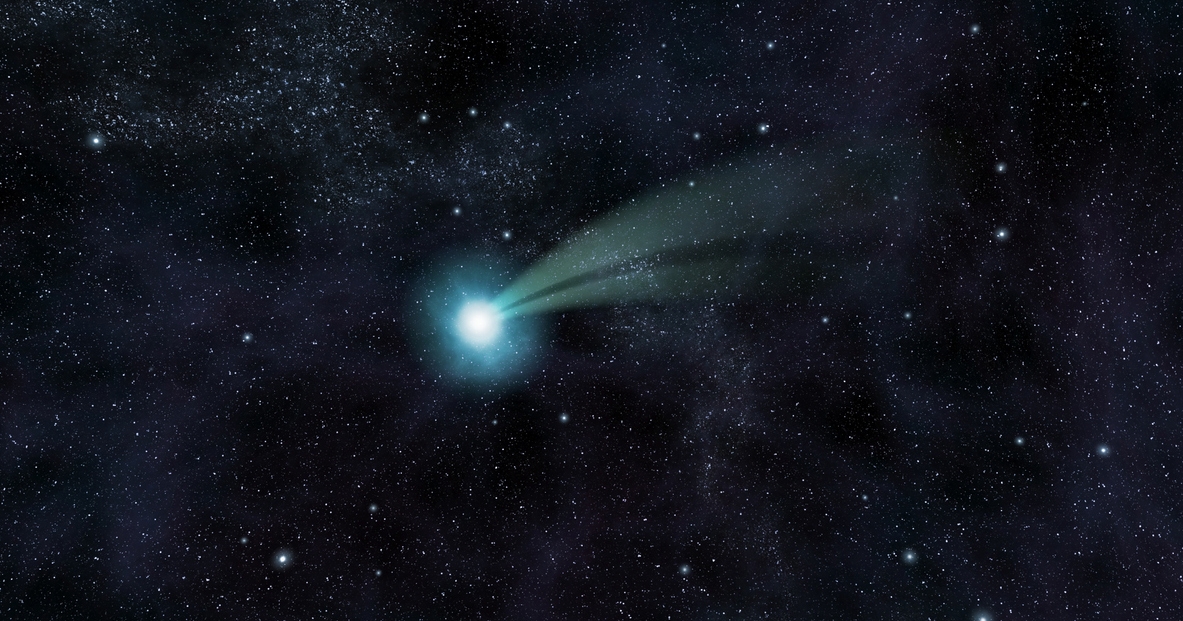
Myth #12: Comet tails always trail behind the comet.
Heat and solar wind, which is the flow of solar wind particles rather than friction, affect a comet’s tail since a comet in space is devoid of all substance. Solar radiation causes the comet’s volatile components to evaporate and stream out of the nucleus as it moves toward the inner Solar System, dragging dust with it. The streams of gas and dust that are so discharged create a vast, incredibly thin atmosphere known as the coma that surrounds the comet. The solar wind and radiation pressure of the Sun put force on the coma, causing a massive tail to form that points away from the Sun. [13]
Myth #13: The moon is very reflective.
There are also many people who believe that the moon is really reflective. But in reality, the moon only reflects around 12% of the light from the Sun. In comparison, the Earth reflects 39% of the light from the sun. In our solar system, Saturn’s moon Enceladus is the most reflective planetary body as it reflects 99% of the sunlight that falls on it back into space. This is because it is mostly made of ice, similar to many moons of the outer solar system. Therefore, if our moon was as reflective as Enceladus, a full moon would look like having another Sun in the night sky. [13]
Myth #14: A star is flinging comets at Earth.
A death star known as Nemesis is said to be lurking in the solar system’s furthest regions and periodically hurling hazardous comets at Earth. Some researchers have suggested that such a star exists in order to explain why mass extinctions on Earth appear to occur on a regular basis. According to the idea, as Nemesis travels through space, it frequently disturbs comets in the distant Oort Cloud, propelling a significant number of the icy wanderers toward Earth. [14]
The issue with that theory, according to a study, is that Earth provides no proof that massive impacts have happened on a regular basis. It appears that the alleged pattern is a statistical artifact.
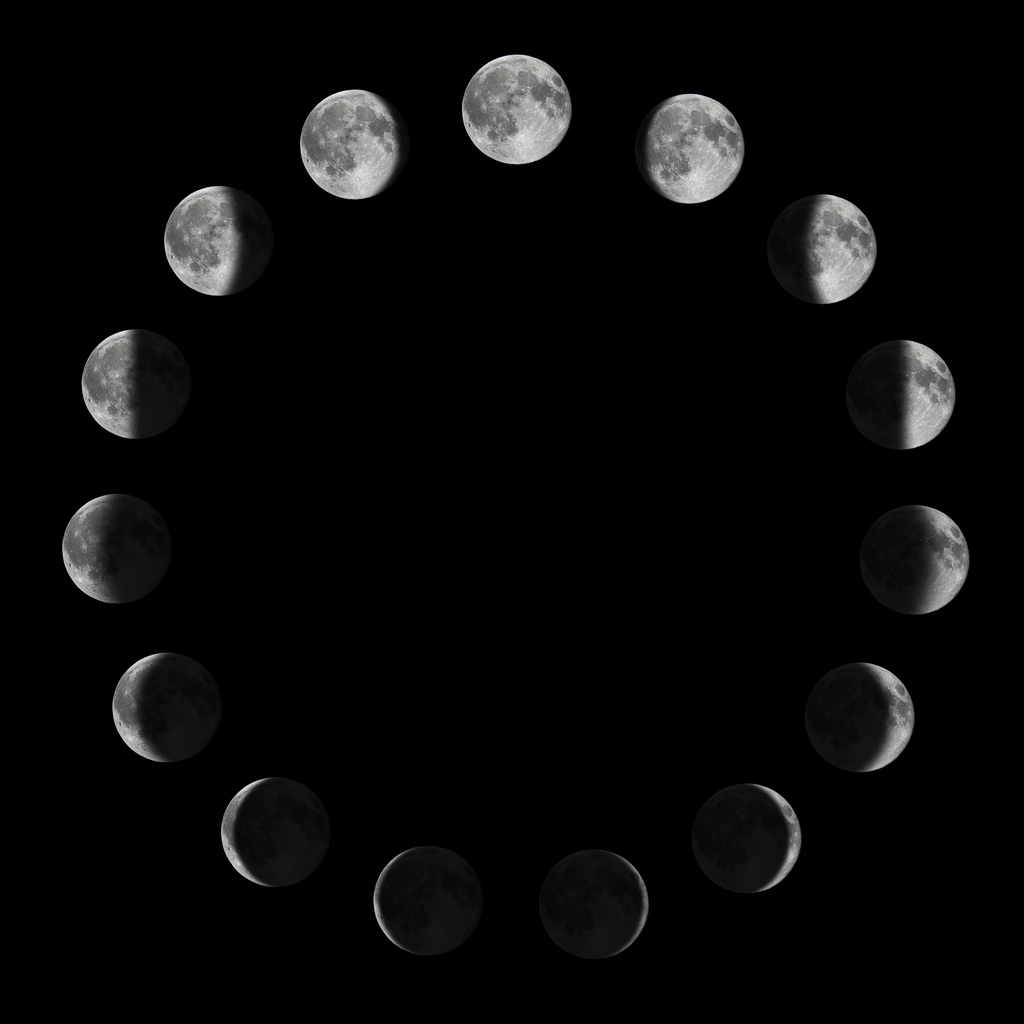
Myth #15: Moon phases are caused by the shadow of the Earth.
It’s a popular fallacy that the moon’s phases are caused by the sun casting the earth’s shadow on the moon’s surface. It actually occurs far less frequently than you may imagine because of the tilt of the globe, and when it does, it is known as an eclipse.
On the other hand, lunar phases are brought on by the moon’s alignment with the sun. Because the dark portion of the moon is the half that is facing away from the sun, when we see a portion of it darkened and invisible, it is not because of the earth’s shadow. We experience distinct phases of the moon depending on the moon’s position in regard to us, even though half of the moon is constantly in darkness and half is always light. [15]
Conclusion
These are some of the myths about space that many people think are actual facts. It is easy to believe most of these myths as they are backed by good explanations. However, stronger scientific studies and research are done in order to debunk them and provide factual clarifications. There are indeed a lot of misconceptions about space, and most of them are brought about by science-fiction movies that are bad in science, as well as tabloid papers.
Therefore, when gathering data about certain topics, you need to always be careful and research thoroughly to learn whether or not a piece of information is a fact or just a myth. We hope this post helped you in clarifying some of the most common space myths out there.
References
[1] New World Encyclopedia, E. (2019, January 8). Outer Space. New World Encyclopedia. Retrieved August 12, 2022, from https://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/outer_space
[2] Howell, E. (2022, February 17). What is space? Space.com. Retrieved August 12, 2022, from https://www.space.com/24870-what-is-space.html
[3] Baird, C. S. (2012, December 17). How long can a human in outer space last without a spacesuit before exploding? Science Questions with Surprising Answers. Retrieved August 12, 2022, from https://www.wtamu.edu/~cbaird/sq/2012/12/17/how-long-can-a-human-in-outer-space-last-without-a-spacesuit-before-exploding/
[4] BBC, E. (2019, October 7). Five things we get wrong about space. BBC Bitesize. Retrieved August 12, 2022, from https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/articles/z7y6gwx
[5] The StarChild Team. (2001). How can the sun “burn”? NASA. Retrieved August 12, 2022, from https://starchild.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/StarChild/questions/question36.html
[6] Perfetto, I. (2022, February 8). Explainer: Is there sound in space? Cosmos. Retrieved August 12, 2022, from https://cosmosmagazine.com/space/astronomy/explainer-is-there-sound-in-space/
[7] SurpriseBit. (2017). Myth busting #1: You can’t travel through an asteroid belt? Steemit. Retrieved August 12, 2022, from https://steemit.com/myth/@surprisebit/myth-busting-1-you-can-t-travel-through-an-asteroid-belt
[8] Royal Museums Greenwich, E. (2022). Moon landing conspiracy theories, debunked. Royal Museums Greenwich. Retrieved August 12, 2022, from https://www.rmg.co.uk/stories/topics/moon-landing-conspiracy-theories-debunked
[9] Mosher, D. (2017, August 3). 17 ‘facts’ about space and earth that you thought were true – but have been debunked by Science. Business Insider. Retrieved August 12, 2022, from https://www.businessinsider.com/false-space-facts-misconceptions-2017-7
[10] Kaufman, M. (2022, June 22). Black holes aren’t evil cosmic vacuum cleaners, and other misconceptions. Mashable. Retrieved August 12, 2022, from https://mashable.com/article/black-holes-misconceptions-space-milky-way-image
[11] Siegel, E. (2021, December 10). No, black holes don’t suck everything into them. Forbes. Retrieved August 12, 2022, from https://www.forbes.com/sites/startswithabang/2019/06/19/no-black-holes-dont-suck-everything-into-them/?sh=5a9521ee2b01
[12] Ward, A. (2019, April 26). 10 misconceptions about space. Mental Floss. Retrieved August 12, 2022, from https://www.mentalfloss.com/article/67873/10-misconceptions-about-space
[13] Nevres, M. Ö. (2022, May 13). Top 21 common misconceptions about space. Our Planet. Retrieved August 12, 2022, from https://ourplnt.com/common-misconceptions-space/
[14] Space.com, S. (2011, August 8). Nemesis no more? comet-hurling ‘death star’ most likely a myth. Space.com. Retrieved August 12, 2022, from https://www.space.com/12559-nemesis-star-nibiru-existence-comet-impact.html
[15] Vork, L. (2019, March 2). What causes phases of the Moon? Sciencing. Retrieved August 12, 2022, from https://sciencing.com/causes-phases-moon-5379166.html