Intelligence may be defined in various ways, such as self-awareness, reasoning capability, comprehension, learning capacity, critical thinking, etc. Additionally, there are other subtypes of intelligence, including social and academic intelligence. Because of this, defining intelligence is difficult and may cause controversy. Having a higher-than-average capacity for cognition is often seen as being clever. It differs from person to person and manifests itself in their conduct.
Four historical methods, namely thinking humanely, thinking logically, behaving humanely, and acting logically, can be used to describe intelligence in the context of AI. While the other two methods focus on conduct, the first two are concerned with cognition and reasoning. The ability to smoothly complete activities that typically require human intellect is the primary goal of AI systems. Four historical methods, namely thinking humanely, thinking logically, behaving humanely, and acting logically, can be used to describe intelligence in the context of AI. While the other two methods focus on conduct, the first two are concerned with cognition and reasoning. The ability to smoothly complete activities that typically require human intellect is the primary goal of AI systems.
Be sure to check out our in-depth guide to Artificial Intelligence
There seems to be artificial intelligence (AI) everywhere. AI has evolved into a technology that is so difficult to ignore that tech companies cannot stop talking about it. It is altering everything from education to healthcare. Even though AI is currently the subject of extensive discussion, it is not a recent development. Since ancient times, artificial intelligence has developed into the revolutionary technology it is today.
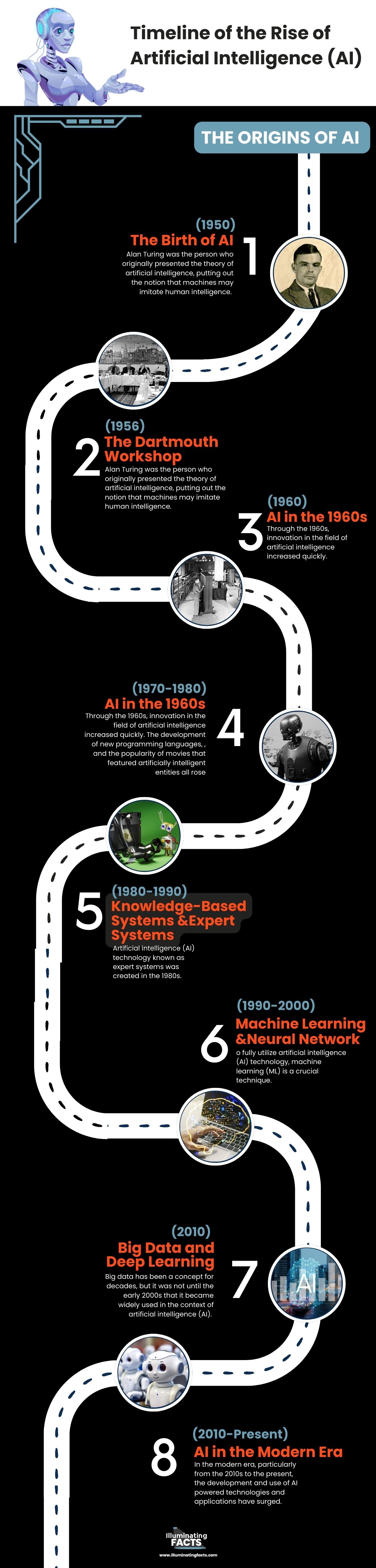
The timeline that highlights key milestones and developments in the rise of AI
John McCarthy, the founder of artificial intelligence, first used the phrase “artificial intelligence” in 1956. However, the AI revolution started a few years earlier, in the 1940s.
AI is now more prevalent in people’s daily lives. Smartwatches, recommendation engines on streaming services like Netflix and YouTube, innovative home systems, voice assistants, messaging platforms, automated customer assistance, and other day-to-day commercial initiatives are just a few examples of platforms where AI is being used.
Where exactly does AI fit within the history of artificial intelligence?
Unquestionably, artificial intelligence has evolved into a trustworthy tool for working. It is used in large data analysis and processing, customer service chatbots, search engine algorithms, and the simplification of complicated procedures.
Additionally, a partnership between AI and cybersecurity has been formed. It grows more capable of initiating preventative actions against a cyber assault as it gathers more knowledge about the threats and vulnerabilities that develop over time.
The Origins of AI (1950s-1960s)
1950s – The Birth of AI
Alan Turing was the person who originally presented the theory of artificial intelligence, putting out the notion that machines may imitate human intelligence. The “Turing Test” was developed as a result of this to evaluate a machine’s capacity to display intelligent behavior that is comparable to or impossible to differentiate from human behavior.
The most well-known computer scientist and mathematician in the world, Alan Turing, has proposed yet another test of artificial intelligence. The goal was to see whether a machine could reason and make judgments just as intelligently and reasonably as a human person. During the exam, a questioner must determine which response is from a human and which is from a computer. Therefore, the machine would pass the test of being indistinguishable from a human being if the interrogator could not tell them apart.
1956 – The Dartmouth Workshop
John McCarthy is the highlight of our history of Artificial Intelligence. His proposal for the Dartmouth Conference, the first-ever AI conference held in 1956, is where he first used the phrase “artificial intelligence.” He was an American computer scientist. The goal was to create a machine that was able to reason and think like a human. He was confident that this scientific discovery will be made within the next 5000 years. In 1958, he also developed the Lisp computer language, which eventually became the norm for AI programming.
AI in the 1960s
Through the 1960s, innovation in the field of artificial intelligence increased quickly. The development of new programming languages, the development of robots and automatons, academic study, and the popularity of movies that featured artificially intelligent entities all rose. The significance of AI in the latter part of the 20th century was amply illustrated by this.
Early AI research and development
The history of AI as a whole has been significantly influenced by the Dartmouth Conference. It promoted the growth of new technologies and methodologies while establishing AI as an area of study. The group’s goal for AI called for the development of intelligent robots that could think, learn, and communicate much like people. This idea spurred a surge of study and invention in the area. After the meeting, John McCarthy and his associates created LISP, the first programming language for artificial intelligence. This language, which is still used today, served as the basis for AI research.
Early AI programs and systems
Logic Theorist
Computer software Logic Theorist was created in 1956 by Cliff Shaw, Allen Newell, and Herbert A. Simon. It has been referred to as “the first artificial intelligence program” since it was the first software application specifically designed to execute automatic reasoning. 38 of the first 52 theorems of Whitehead and Russell’s Principia Mathematica were proven by logic theorists, who also discovered fresh and better proofs for several of the theorems.
General Problem Solver (GPS)
The General Problem Solver (GPS) software was developed by Herbert A. Simon, J. C. Shaw, and Allen Newell (RAND Corporation) in 1957 to serve as a general-purpose problem-solving tool. The GPS uses means-ends analysis as opposed to the previous Logic Theorist effort.
Early computer programs like GPS, which constructed a directed graph with sources (axioms) and sinks (desired conclusions), could solve problems defined as collections of well-formed formulae or Horn clauses. It distinguished between problem-solving methodology and problem knowledge. Although it was capable of handling straightforward formalized issues like the Towers of Hanoi, its exponential search complexity made it difficult to solve real-world issues. The AI Soar architecture was developed from GPS.
The AI Winter (1970s-1980s)
A major slowdown in research and development in artificial intelligence (AI) is referred to as the “AI Winter of the 1980s.” After a decade of substantial advancement in AI research and development, from 1974 to 1993, there was a period of stasis. The 1960s AI boom was characterized by an explosion in AI study and use. The AI winter, which happened in the 1980s, came next, though.
This was partially caused by the fact that many of the AI initiatives created during the AI boom fell short of their goals. The lack of advancement in the area was gradually demoralizing the AI research community. As a result, funding was reduced, forcing many AI researchers to give up on their endeavors and quit the field completely.
The 1980s’ “AI Winter” was marked by a sharp fall in financing for AI research and a general lack of enthusiasm among investors and the general public. As a result, the number of AI projects being created significantly decreased, and many of the research programs that were still ongoing were unable to make substantial progress for lack of funding. The field of artificial intelligence survived the AI Winter’s difficulties. During this time, several academics continued to work on AI-related projects and made significant progress, including the creation of neural networks and the beginnings of machine learning. However, development in the area was sluggish, and interest in AI did not start to take up again until the 1990s (more on that later).
The AI Winter of the 1980s, which highlighted the difficulties and constraints of AI research and development, was a critical turning point in the history of AI. It also acted as a warning to investors and legislators, who realized that the excitement surrounding AI may occasionally be exaggerated and that continued investment and dedication would be necessary for advancement in the area.
Knowledge-Based Systems and Expert Systems (1980s-1990s)
Artificial intelligence (AI) technology known as expert systems was created in the 1980s. Expert systems are created to emulate a human expert’s decision-making processes in a particular subject area, such as engineering, finance, or medicine. There was a lot of hope and enthusiasm about AI and its potential to revolutionize several sectors during the 1960s and the early 1970s. However, as we described in the last part, the AI winter, which was characterized by a lack of advancement and financing for AI research, subdued this excitement. An important advance in the history of AI was the creation of expert systems.
The quest for practical, scalable, reliable, and measurable uses of artificial intelligence has raised pressure on the AI community. Expert systems were presented as evidence that AI systems could be applied to existing systems and had the potential to be very beneficial to many business and industry sectors. From identifying medical illnesses to forecasting stock prices, expert systems were utilized to automate decision-making processes.
The effectiveness and efficiency of medical diagnosis and treatment might be greatly increased with the application of artificial intelligence (AI). AI systems, for instance, may examine enormous volumes of patient data to spot trends and forecast results, assisting physicians in making better choices. AI also has the potential to automate certain operations, such as the analysis of medical pictures or the processing of electronic health data, freeing up time for physicians and nurses to work on more crucial duties. Healthcare workers may improve care for their patients while also lowering the chance of mistakes by utilizing the power of AI.
One of the main sectors where AI is being used is the banking sector, where many businesses use machine learning algorithms to automate and improve numerous procedures. AI may be used, for instance, to evaluate risk, spot fraud, and improve trading tactics. AI systems can find patterns and forecast outcomes by analyzing vast volumes of data, which would be difficult for a person to do. The application of AI in finance can also assist decrease the need for manual labor, freeing up staff to concentrate on more difficult jobs.
Numerous businesses are attempting to create self-driving cars and intelligent transportation systems, which have the potential to completely transform the transportation industry. By removing human error, self-driving cars, for instance, might drastically lower the frequency of accidents on the road, while intelligent transportation systems could enhance traffic flow and ease congestion. AI might also be used to streamline travel plans and utilize less fuel, improving the effectiveness and sustainability of transportation. The industry’s efficiency and safety might be dramatically increased by applying AI to transportation.
Machine Learning and Neural Networks (1990s-2000s)
To fully utilize artificial intelligence (AI) technology, machine learning (ML) is a crucial technique. Machine learning is sometimes referred to as AI due to its capacity for learning and decision-making, but in truth, it is a subset of AI. Up to the late 1970s, it was a stage in the development of AI. It then split off to continue evolving on its own. Machine learning is now employed in many cutting-edge technologies and has become a crucial response tool for cloud computing and e-commerce.
For many firms today, machine learning is an essential component of contemporary business and research. It helps computer systems perform better over time by using algorithms and neural network models. Without being directly taught to make certain judgments, machine learning algorithms automatically create a mathematical model using sample data, sometimes referred to as “training data.”
A model of how brain cells interact is one of the foundations of machine learning. The model was developed in 1949 by Donald Hebb, who also presented his views on neuronal excitation and communication between neurons in the book “The Organization of Behavior.”
Hebb stated that “when one cell repeatedly assists in firing another, the axon of the first cell develops synaptic knobs (or enlarges them if they already exist) in contact with the soma of the second cell.” Applying Hebb’s ideas to artificial neural networks and artificial neurons, his model can be described as a method of changing the connections between artificial neurons (or nodes) and the changes to individual neurons. When two neurons or nodes are triggered simultaneously, their association becomes stronger than when they are activated separately. When describing these associations, the term “weight” is employed, and nodes/neurons that tend to be both positive and negative are said to have very positive weights. Nodes with opposing weights acquire substantial negative weights, such as 11=1, -1x-1=1, and 11=-1.
Big Data and Deep Learning (2010s)
The explosion of data and the availability of large datasets for AI training
Big data has been a concept for decades, but it was not until the early 2000s that it became widely used in the context of artificial intelligence (AI). Volume, Velocity, and Variety are the three essential requirements for data to be deemed huge. The term “volume” refers to the data set’s overall size, which might be in the terabyte, petabyte, or even bigger range. The term “velocity” describes the rate at which data must be created and processed. For instance, real-time data generated by IoT devices or social media platforms must be handled promptly. Additionally, diversity refers to the many data kinds that are produced, such as structured, unstructured, and semi-structured data. Before the introduction of big data, AI was constrained by the quantity and caliber of data accessible for machine learning training and testing.
Deep learning algorithms and architectures have seen substantial advancements, which have led to significant advancements in artificial intelligence (AI). Image recognition and computer vision tasks have been transformed by convolutional neural networks (CNNs), which automatically learn and extract hierarchical properties from images. They are quite good at recognizing faces, identifying objects, and classifying images. The purpose of recurrent neural networks (RNNs) is to process sequential input, including speech and text. Due to their ability to gather dependencies and contextual data from previous inputs, they are perfect for applications like language modeling, machine translation, and sentiment analysis.
Utilizing Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), which provided a novel notion by pitting two neural networks against one another, is another breakthrough. GANs are made up of a discriminator network that learns to distinguish between real and fake data and a generator network that learns to produce false data. GANs have demonstrated impressive abilities in data augmentation, picture generation, and style transfer. Transformer Networks have also altered the task of natural language processing (NLP). These models use self-attentional processes to capture contextual interactions between words or tokens in a sequence, which enables them to effectively handle long-range dependencies. Transformers have played a significant role in the advancement of machine translation, language understanding, and text generation issues.
The use of AI in several fields has produced notable developments in autonomous cars, picture recognition, and natural language processing (NLP). Deep learning methods like convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have revolutionized applications like object identification, picture classification, and facial recognition in the fields of image recognition and computer vision. Machine translation, sentiment analysis, chatbots, and voice assistants have all benefited from the incorporation of AI into NLP since it has considerably enhanced language understanding and creation. Moreover, the incorporation of AI into autonomous cars has revolutionized transportation by improving observation, planning, and decision-making skills for secure control and navigation.
Overall, the use of AI to image identification, natural language processing, and autonomous vehicles has created new opportunities across several sectors. As a result of these developments, technology is becoming more effective, user-friendly, and secure. We predict more developments in these fields as a result of continuous AI improvements, which will spur innovation and fundamental societal transformations.
AI in the Modern Era (2010s-Present)
The rapid growth of AI-powered technologies and applications
In the modern era, particularly from the 2010s to the present, the development and use of AI-powered technologies and applications have surged. Some of the reasons for this increase include the availability of vast datasets for training AI models, advancements in computing power, and the development of ever-more-complex algorithms.
AI has found use in several industries, including banking, healthcare, transportation, entertainment, and more. AI is utilized in healthcare for drug development, medical imaging analysis, and customized treatment. AI algorithms are used in finance for risk analysis, algorithmic trading, and fraud detection. AI plays a significant role in the navigation and object identification of autonomous vehicles and drones. AI-powered virtual assistants that can respond to voice requests and carry out a variety of activities, like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant, have proliferated in many homes.
Advancements in areas
Robotics, virtual assistants, and autonomous systems have made tremendous strides in the contemporary period thanks to AI technology.
Robotics has advanced significantly, and machines are now more powerful and adaptable. Industrial robots are being employed more often in production processes as they become more effective. Cobots, or collaborative robots, may aid people in jobs that call for strength and accuracy while working side by side with them. Robot perception and manipulation abilities have also been improved by AI algorithms, making them better able to comprehend and interact with their surroundings.
The sophistication and integration of virtual aids into our daily lives have increased. These AI-powered agents are capable of comprehending spoken language, responding to voice instructions, and carrying out duties like appointment booking, question-answering, and managing smart home devices. Virtual assistant technologies have seen significant investment from companies like Apple, Amazon, and Google, who are continuously expanding their capabilities.
The development of autonomous systems, such as drones and self-driving cars, has also seen significant advancements. Self-driving vehicles have been tested and developed by several companies, and they have already been deployed in open road trials. These cars rely on AI systems for vision, decision-making, and safe navigation. Drones equipped with AI technology are used for tasks including aerial photography, delivery services, and infrastructure assessments.
Ethical Considerations and debates surrounding AI
AI-related technologies have sparked ethical questions, such as prejudice and privacy concerns. By having greater mistake rates for women and those with darker skin tones in facial recognition systems, biases in AI systems might reinforce existing stereotypes. To solve this problem, initiatives are being made to increase dataset variety, algorithmic fairness, and transparency. Because AI systems collect so much data, privacy issues are raised, necessitating careful handling and protection. The benefits of AI and user privacy are now balanced through discussions and laws. Global discussions have been prompted by the ethical implications of AI in areas including autonomous weaponry, algorithmic decision-making, and employment displacement. In the current era of AI, creating ethical frameworks and norms that include openness and human monitoring is a critical task.
Impact on Industries and Society
1. Maps and Navigation
Traveling has been greatly enhanced by AI. You may now use Google or Apple Maps on your phone and punch in your location rather than relying on printed maps or directions. So how does the application determine its destination? What is more, the best route, traffic jams, and road barriers? Before recently, the only GPS technology available was satellite-based, but artificial intelligence is now being included to provide consumers with a significantly improved experience. With the use of machine learning, the algorithms can recognize and comprehend home and building numbers as well as the boundaries of the structures they have learned, resulting in improved map visualization. For the program to suggest a route that avoids traffic jams and barricades, it has also been taught to comprehend and recognize variations in traffic flow.
2. Facial Detection and Recognition
We now use artificial intelligence regularly in the form of virtual filters on our faces while shooting photos and facial IDs to unlock our phones. Any human face is recognized in the former thanks to face detection. The latter makes use of facial recognition to identify a particular face. Government buildings and airports also utilize facial recognition for monitoring and security.
3. Text Editors or Autocorrect
When you were a student, you could have used software like Grammarly to proofread your final paper before turning it in to your instructor, and you might still use it now to double-check the spelling in an email to your employer. Another illustration of artificial intelligence is this. In word processors, messaging applications, and almost every other written media, AI algorithms utilize machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing to identify erroneous language usage and offer changes. Together, linguists and computer scientists teach computers grammar in the same way that you were taught it in school. Because the algorithms were trained using high-quality linguistic data, the editor will recognize when you use a comma inappropriately.
4. Search and Recommendation Algorithms
Have you ever noticed that when you wish to watch a movie or purchase online, the recommendations made to you frequently match your hobbies or most recent searches? By monitoring your online activities, these clever recommendation algorithms have gradually come to understand your behavior and preferences. The user provides the data upfront, which is then saved and subject to machine learning and deep learning for analysis. After that, it can typically forecast your tastes and make suggestions for what you might like to buy or listen to next.
5. Chatbots
Consumer service interactions may be time-consuming and frustrating for the consumer. It is a costly, ineffective department that is difficult to manage for businesses. AI chatbots are one increasingly common artificially intelligent remedy for this. Machines can receive and track orders, answer commonly asked inquiries, and route calls thanks to programmed algorithms. Natural language processing (NLP) is used to train chatbots to mimic the conversational patterns of customer service professionals. Modern chatbots do not need certain input forms, like yes or no questions, anymore. They can respond in-depth to challenging queries. If you rate the response, you received poorly, the bot will recognize its error and avoid it in the future, guaranteeing optimum client pleasure.
Future Outlook and Challenges
Exploration of future trends in AI
AI Ethics. AI ethics is a set of moral guidelines and methods meant to guide the creation and ethical application of artificial intelligence technologies. Organizations are beginning to create AI codes of ethics as AI has become ingrained in goods and services. A policy declaration that explicitly defines the function of artificial intelligence as it relates to the advancement of the human race is known as an AI code of ethics, also known as an AI value platform. An AI code of ethics is intended to offer stakeholders direction when making moral choices involving the use of artificial intelligence.
Explainable AI. As AI systems get more complex and potent, transparency and interpretability are becoming more and more crucial. Explainable AI aims to create methods and tools that enable users to understand and evaluate the decisions made by AI systems. This encourages responsibility, assures fairness, and contributes to the development of trust in AI applications.
Responsible AI development. The design and implementation of AI systems must be in line with societal norms and promote individual and collective well-being. Making sure AI is used in a way that respects human rights, does not damage anyone, and takes into consideration the broader societal and environmental effects is what is meant by “responsible AI development,” which means doing all of the above.
Challenges and Considerations for AI Adoption
Data Privacy. AI mainly relies on data, and the gathering, storing, and utilization of personal data raise serious privacy problems. When using data for the creation of AI, organizations must traverse the difficulties of gaining consent, safeguarding sensitive information, and maintaining data security. It will be vital to strike a balance between innovation and privacy.
Regulatory Frameworks. As AI develops, regulatory frameworks must keep up to manage the particular difficulties and dangers posed by the technology. To regulate AI research, deployment, and usage, governments and regulatory agencies will need to create rules and regulations. These structures ought to guarantee responsibility, stop abuse, and provide defense against prejudice and discrimination.
Ethical Guidelines. It is essential to lay out clear ethical guidelines for AI to limit potential harm and ensure responsible adoption. These guidelines ought to address issues like equality, transparency, accountability, and the impact of AI on society. Industry standards and best practices must be created to assist businesses and AI practitioners in making moral judgments.
AI has already had a significant influence on our lives, and as it develops, the world will continue to alter in many different ways. As AI technology advances, the development and adoption of moral AI practices must be given high importance. This includes talking about things like explainability, morality, and responsible growth.
Although AI has a lot of potential, some risks and challenges need to be properly explored. By promoting cooperation between researchers, policymakers, business leaders, and the general public, we can navigate the shifting landscape of AI and realize its potential for social improvement. Through responsible AI research, we may strive toward a future in which AI systems are transparent, answerable, and compatible with human values, ultimately leading to a more inclusive and just society.
Conclusion
Finally, major turning points in the development of artificial intelligence have had a substantial influence on civilization. AI has steadily permeated daily life since the development of the first AI algorithms and the development of expert systems, machine learning, and deep learning. While embracing the advantages of AI, it’s important to address ethical and societal issues including job displacement, privacy, and prejudice. AI has the ability to foster innovation, solve challenging issues, and create ethical frameworks, all of which will help shape a better future by encouraging responsible growth, teamwork, and moral decision-making.