Goosebumps, scientifically known as “piloerection,” are a common physiological response that occurs in humans and various animals. This phenomenon occurs when small muscles, called arrector pili, contract and cause hair follicles to stand upright. While often associated with cold temperatures, goosebumps can also be triggered by various emotions, creating a visible reaction on the skin.
In this post, we unravel the scientific intricacies behind goosebumps and delve into the emotional triggers that prompt this fascinating physiological response. From the autonomic nervous system’s role to the emotional nuances involved, let’s uncover the mystery behind what happens when goosebumps emerge.
The Science Behind Goosebumps
When it comes to understanding goosebumps, science takes center stage. These small, raised bumps on our skin have a profound explanation rooted in human physiology. Let’s look at how it occurs:
| Process | Description |
| Trigger | External factors like cold, fear, or strong emotions. |
| Nervous System | The autonomic nervous system detects triggers. |
| Hormonal Response | It releases hormones, such as adrenaline. |
| Muscle Contraction | Arrector pili muscles contract. |
| Hair Follicle Movement | Muscles pull on hair follicles, causing them to stand upright. |
| Skin Appearance | The skin’s surface appears raised, forming goosebumps. |
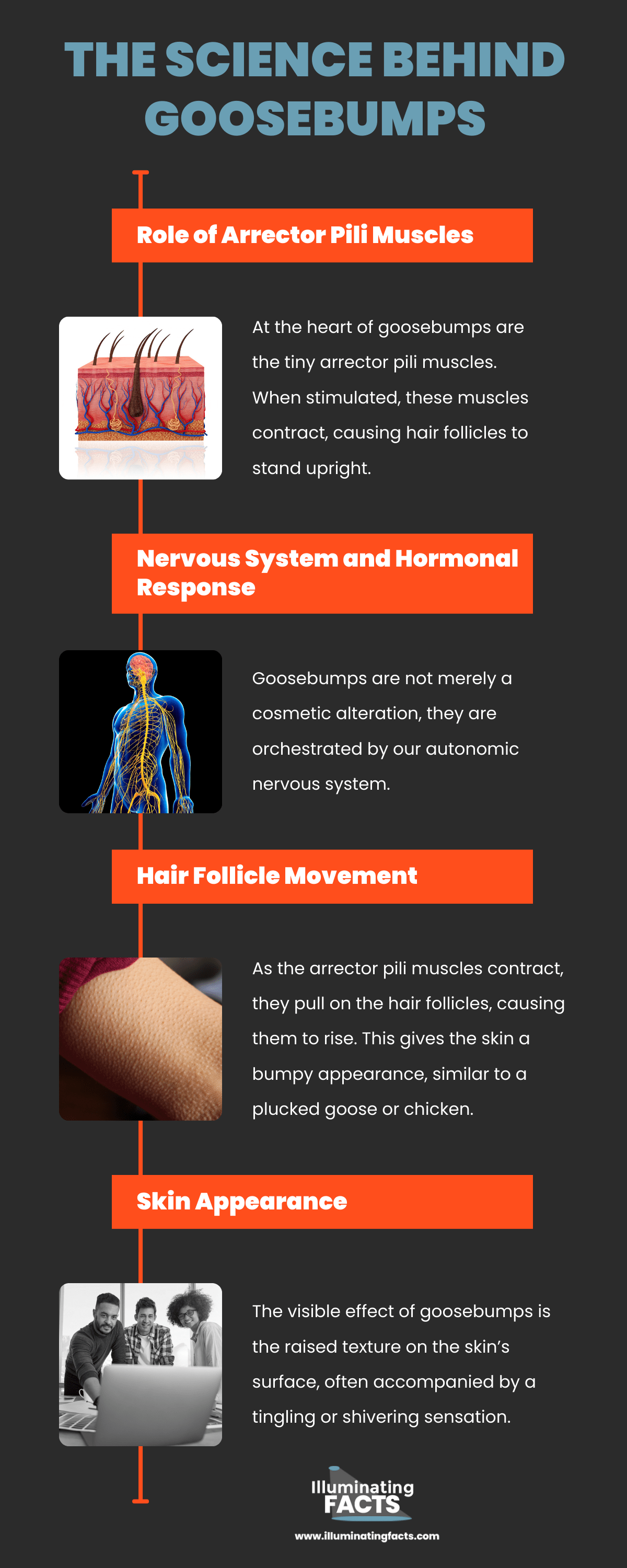
Role of Arrector Pili Muscles
At the heart of goosebumps are the tiny arrector pili muscles. [1] When stimulated, these muscles contract, causing hair follicles to stand upright. This is the primary reason why we notice goosebumps as hair on our skin appears to “stand on end”.
Nervous System and Hormonal Response
Goosebumps are not merely a cosmetic alteration, they are orchestrated by our autonomic nervous system. When exposed to triggers like cold temperatures or strong emotions, this system sends signals that activate the arrector pili muscles. [2]
Hair Follicle Movement
As the arrector pili muscles contract, they pull on the hair follicles, causing them to rise. This gives the skin a bumpy appearance, similar to a plucked goose or chicken.
Skin Appearance
The visible effect of goosebumps is the raised texture on the skin’s surface, often accompanied by a tingling or shivering sensation.
Causes and Triggers
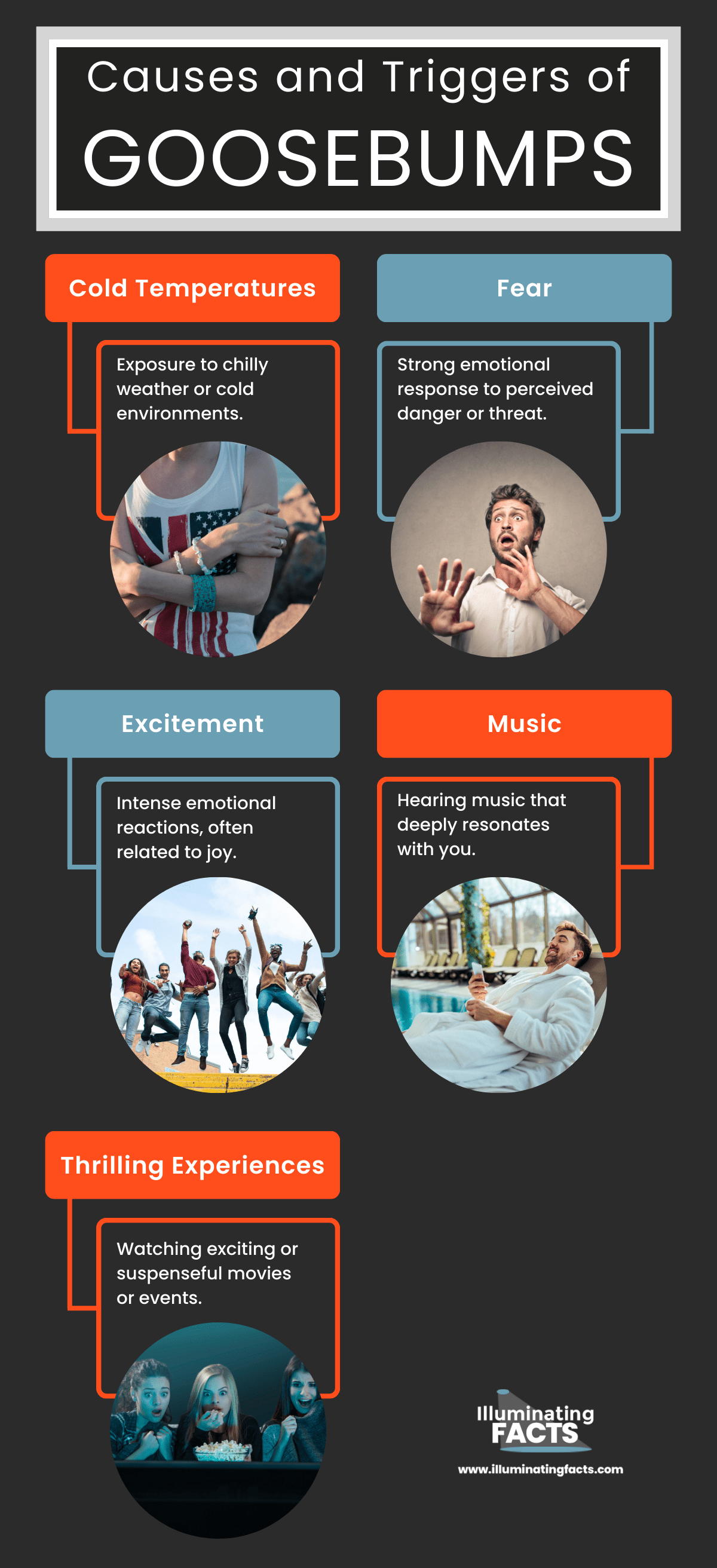
Goosebumps can be prompted by various causes and Triggers. From the chill of a crisp winter’s night to the thrill of a suspenseful movie scene, goosebumps can emerge in various scenarios. Understanding these factors sheds light on the intricacies of our body’s responses.
| Causes and Triggers | Description |
| Cold Temperatures | Exposure to chilly weather or cold environments. |
| Fear | Strong emotional response to perceived danger or threat. |
| Excitement | Intense emotional reactions, often related to joy. |
| Music | Hearing music that deeply resonates with you. |
| Thrilling Experiences | Watching exciting or suspenseful movies or events. |
Cold Temperatures
Exposure to chilly weather or cold environments is a common trigger for goosebumps. [3] When your body senses the cold, it tries to conserve heat by raising hairs on your skin, causing goosebumps.
Emotional Responses
Goosebumps aren’t always linked to physical sensations, they can also be triggered by strong emotional responses. Two prominent emotions associated with goosebumps are:
Fear
Intense emotions like fear can trigger goosebumps. [4] This is connected to the body’s “fight or flight” response, where adrenaline is released. It causes the release of adrenaline, which can cause your arrector pili muscles to contract, leading to goosebumps.
Excitement
Intense excitement or heightened emotions, whether from watching an exhilarating movie scene or experiencing a thrilling event, can also trigger goosebumps. These emotional responses can lead to the same physiological reactions as fear.
Other Circumstances
In addition to cold temperatures and emotional responses, goosebumps can be provoked by various other circumstances. These may include sudden changes in temperature, or certain medical conditions. [5] Such situations can evoke a physiological response leading to goosebumps. Even music that deeply resonates with you can give you piloerection. Frozen by the pop icon Madonna or Lilac Wine by Jeff Buckley are good examples.
Evolutionary Perspective
The study of goosebumps offers a fascinating insight into the intertwined history of humans and their distant, furrier ancestors. While today’s humans might not rely on them for warmth, understanding the evolutionary perspective of goosebumps reveals an intriguing tale of adaptation and heritage. From providing insulation in furry creatures to offering a glimpse into our own evolutionary past, the story of goosebumps is more than just skin-deep.
Purpose in Animals
Goosebumps serve a practical function in animals, particularly those with fur or feathers. When an animal’s hair or feathers stand on end due to muscle contractions around hair follicles (the arrector pili muscles), it can help trap a layer of air beneath the hair, providing insulation. In response to cold or fear, this mechanism helps animals stay warm by creating an extra layer of insulation [6] or making them appear larger and more intimidating to potential predators.
Evolutionary Significance in Humans
In humans, the purpose of goosebumps is more vestigial. While the physiological response remains from our evolutionary ancestors, our body hair is much finer and less dense than that of furry animals. [7] So, goosebumps in humans no longer serve a significant insulating function. Instead, they represent a remnant of our evolutionary history, a reminder of the time when our ancestors had thicker body hair. In modern humans, goosebumps are more prominently associated with emotional responses, often manifesting during moments of fear, excitement, or intense emotional experiences.
Evolutionary Aspect | Purpose in Animals | Evolutionary Significance in Humans |
Thermoregulation | Provides insulation in fur-covered animals | Less relevant due to reduced body hair in humans |
Emotional Signals | Indicates emotional states or readiness to confront threats | May serve as a residual response to emotional stimuli in humans |
Enhanced Sensation | Increases sensory perception in response to environmental changes | Contributes to heightened awareness and alertness in humans |
Medical and Health Aspects
Goosebumps are a common physiological response, generally do not pose harm to individuals. They are a natural and temporary occurrence that usually subsides once the triggering stimulus diminishes. While generally harmless, a closer study can offer valuable insights into one’s health and well-being. There are some medical conditions and situations in which goosebumps can be related. Knowing their connection can be crucial in a threatening situation.
Are Goosebumps Harmful?
In most cases, experiencing goosebumps is a natural physiological response to external stimuli, and it is not inherently harmful. [8] However, chronic or excessive goosebumps without apparent triggers could indicate underlying medical issues that should be addressed by a healthcare professional.
Relation to Medical Conditions
Goosebumps can be associated with various medical conditions, including but not limited to:
Condition | Relation to Goosebumps | Common Symptoms | Treatment and Management |
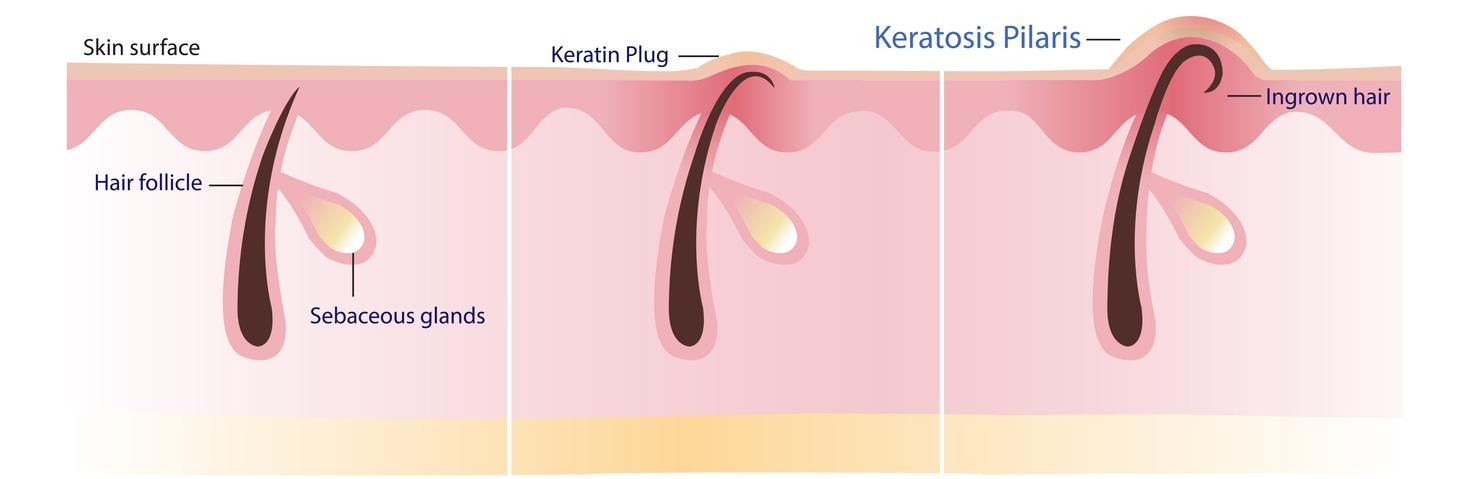
Keratosis Pilaris | Goosebumps-like appearance due to keratin buildup | Small, raised bumps | Exfoliation, moisturizers, topical treatments |
Follicular Eczema | Inflammation of hair follicles makes them look like goosebumps | Itchy, red, inflamed skin | Emollients, topical steroids, avoiding triggers |
Allergic Reactions | Goosebumps as a possible symptom of severe allergies | Hives, itching | Immediate medical intervention (e.g., epinephrine) |
Chronic Stress | Stress hormones triggering goosebumps during prolonged stress | Anxiety, restlessness | Stress management, |
Skin Condition | Relation to Goosebumps | Common Symptoms | Treatment and Management |
Skin Conditions
Certain skin conditions, such as keratosis pilaris or follicular eczema, may cause goosebumps due to irritation or inflammation of hair follicles. These conditions are typically benign but can be unsightly.
Keratosis Pilaris often appears as small, raised bumps on the skin, especially on the arms, thighs, and buttocks. [9] These bumps can resemble goosebumps but are caused by the buildup of keratin. The condition is generally harmless but can be bothersome from a cosmetic perspective.
Follicular eczema, on the other hand, is the condition that affects the hair follicles. [10] Hair in the affected region may stand on end, and inflammation can show up as redness, swelling, itchiness, or warmth. Follicular eczema reactions tend to look like goosebumps that won’t go away.
Allergic Reactions
Severe allergic reactions, such as those to certain foods, insect stings, or medications, can lead to a range of skin symptoms, including hives, itching, and yes, goosebumps. The condition anaphylaxis in particular, is a life-threatening emergency and requires immediate medical intervention.[10]
Chronic Stress
Prolonged or chronic stress can sometimes lead to persistent piloerection (goosebumps) due to the release of stress hormones. Managing stress is essential for overall health. When the body is under prolonged stress, it releases stress hormones like adrenaline and cortisol. These hormones can cause various physical responses, including goosebumps. [11]
While isolated episodes of stress-induced goosebumps are not harmful, chronic stress can contribute to a range of health issues, including cardiovascular problems and mental health disorders.
Medications
Certain medications, such as stimulants or decongestants, may cause goosebumps as a side effect. This is typically not a cause for concern unless accompanied by severe adverse effects.
Medication Class | Medications That May Induce Goosebumps | Possible Side Effects | Management |
Stimulants | Amphetamines, caffeine-based drugs | Goosebumps, increased alertness | Adjusting dosage, consulting healthcare provider |
Decongestants | Pseudoephedrine, phenylephrine (found in some cold meds) | Goosebumps, increased heart rate | Monitoring side effects, consulting a physician |
Stimulants, like amphetamines or caffeine-based drugs, can stimulate the body’s nervous system, leading to goosebumps as a side effect. Decongestants, one of the most prescribed drugs, are a common ingredient in some over-the-counter colds and allergies. They can also cause goosebumps, usually along with increased heart rate and alertness.
While these examples highlight the association of goosebumps with certain conditions, it’s crucial to emphasize that goosebumps themselves are a normal and typically harmless bodily response. They occur as part of the body’s attempt to regulate temperature or respond to emotional or environmental triggers. However, if goosebumps are accompanied by unusual or severe symptoms, or if they persist and cause concern, consulting a healthcare professional is advisable to rule out any underlying medical issues.
Conclusion
The phenomenon of goosebumps is a fascinating blend of science, evolution, and human emotions. While goosebumps often occur as a natural response to cold temperatures or strong emotions, they carry an intricate evolutionary history, reminding us of our animal ancestry.
Despite their unique and sometimes puzzling nature, goosebumps are usually harmless in most situations. However, they can also serve as indicators of underlying medical conditions or severe allergic reactions, emphasizing the importance of paying attention to these seemingly ordinary bodily responses. Understanding the science and significance of goosebumps not only adds depth to our knowledge of our own bodies but also provides insights into our evolutionary heritage.
So, the next time you experience those tiny raised bumps on your skin, remember that they are a remarkable reminder of the intricate interplay between our biology and our environment.
References
- What is an Arrector pili muscle? (with pictures). (n.d.). The Health Board. https://www.thehealthboard.com/what-is-an-arrector-pili-muscle.htm
- The hidden triggers: Why your skin gets Goosebumps. (2022, August 10). Derma Essentia. https://www.dermaessentia.com/blogs/knowledge/goosebumps
- Why do humans get “goosebumps” when they are cold, or under other circumstances? (2003, September 1). Scientific American. https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/why-do-humans-get-goosebu/
- Fecht, S. (2011, October 28). FYI: Why do we get Goosebumps and chills when we’re scared? Popular Science. https://www.google.com/amp/s/www.popsci.com/science/article/2011-10/fyi-why-do-we-get-goose-bumps-and-chills-when-were-scared/%3famp
- Booth, S. (2019, June 10). What causes Goosebumps? WebMD. https://www.webmd.com/skin-problems-and-treatments/goosebumps-causes
- The role of Piloerection in primate Thermoregulation. (2013, October 31). Karger Publishers. https://karger.com/fpr/article/85/1/1/138688/The-Role-of-Piloerection-in-Primate
- Desai, R. (2020, August 17). Why we get Goosebumps. The Swaddle. https://theswaddle.com/why-we-get-goosebumps/
- Why do certain experiences give us Goosebumps? (1970, January 1). HowStuffWorks. https://science.howstuffworks.com/life/inside-the-mind/human-brain/goosebumps.htm
- Keratosis pilaris – Symptoms and causes. (2022, December 23). Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/keratosis-pilaris/symptoms-causes/syc-20351149Rees, M. (n.d.). What to know about follicular eczema: Symptoms and treatment. Medical and health information. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/follicular-eczema#symptoms
- Anaphylaxis: Symptoms & treatment. (n.d.). Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/8619-anaphylaxis
- The surprising reason why we get goosebumps – Times of India. (2019, October 14). The Times of India. https://www.google.com/amp/s/m.timesofindia.com/life-style/health-fitness/health-news/the-surprising-reason-why-we-get-goosebumps/amp_articleshow/71580544.cms