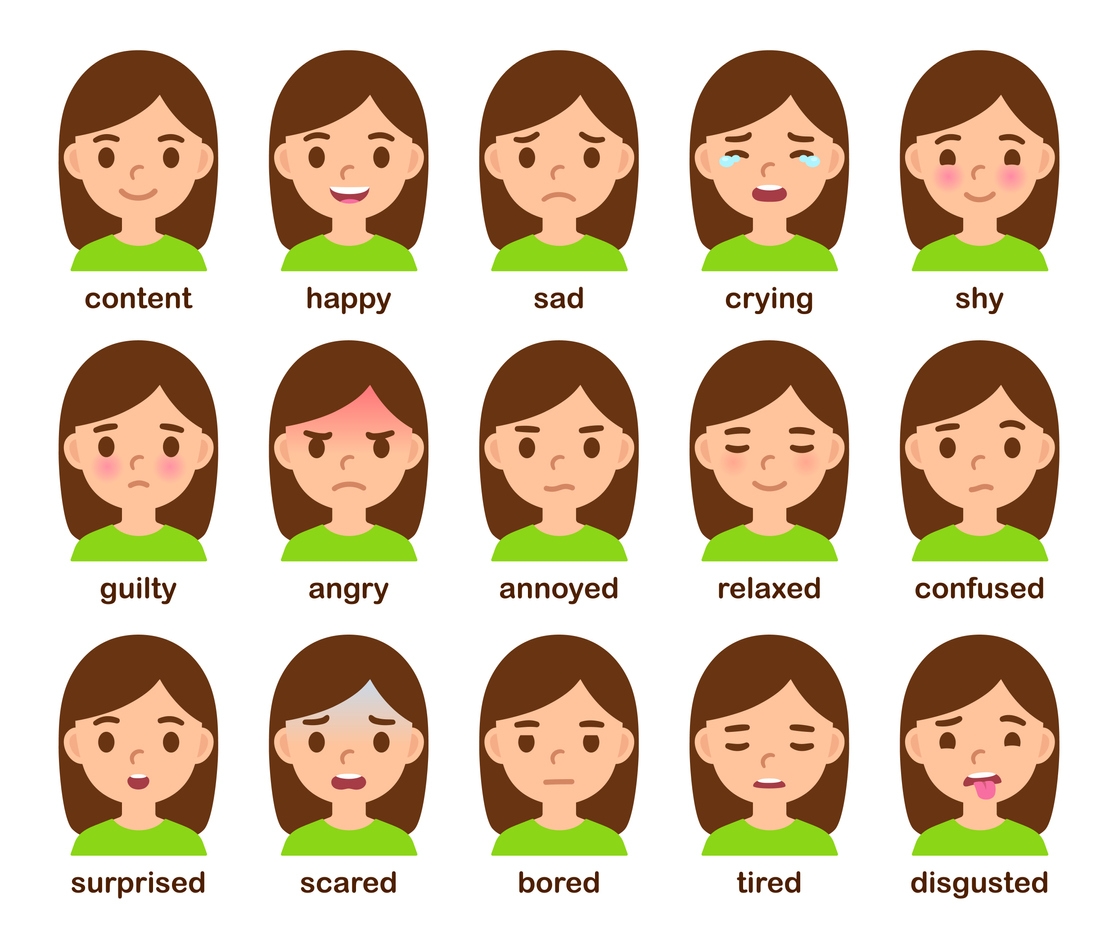
Emotions are the intricate and powerful forces residing within us that drive currents of human experience. Defined as complex responses to internal and external stimuli, these nuanced feelings color our life. Ranging from joy to sorrow, fear to love, emotions encompass a vast spectrum. They shape our thoughts, our actions, and the very essence of who we are. Hence often drive how we think and interact with the world.
Unraveling the mechanisms that govern our emotional experiences involves delving into the intricate landscape of psychology. These psychological processes involve intricate interplays between various brain compartments, neurotransmitters, and cognitive functions. But first you must first have a clear idea of what emotions are. This post will tell you everything about human emotions. From what they are to the intricate tapestry that binds our feelings to our behaviors, you’ll learn everything below.
What Are Emotions?
Emotions are complex and multifaceted mental states that reflect our internal reactions to various stimuli and situations. [1] They are deeply ingrained in our human nature, serving as powerful communicators, conveying information about our needs, desires, and the world around us.
Different Types of Emotional Responses
Spanning a broad spectrum, emotional responses are as diverse as the human experience itself. The emotional landscape is rich and complex, with nuanced variations reflecting the intricacies of our inner lives. [2] From the warmth of happiness to the depths of sadness, from the surge of excitement to the grip of fear, each type of emotion offers a unique lens through which we perceive and interact with the world.
| Emotion | Description |
| Happiness | A state of well-being, often accompanied by joy and contentment. |
| Anger | A strong emotional response to perceived threats, injustice, or frustration. |
| Sadness | A feeling of sorrow, often triggered by loss, disappointment, or grief. |
| Fear | A natural response to potential danger, characterized by anxiety and caution. |
| Surprise | An unexpected reaction to sudden, unforeseen events or revelations. |
| Disgust | A strong aversion to offensive or unpleasant stimuli, often related to repulsion. |
These descriptions provide a brief overview of each emotion and their common triggers, offering a simplified understanding of the rich world of human feelings.
Classification of Emotions
Emotions are complex, and to better understand them, we classify them into two categories: primary and secondary emotions. [3]Each serves distinct roles in our psychological landscape.
| Type of Emotion | Description | Examples |
| Primary Emotions | Emotions that are immediate and instinctive responses to stimuli | Personal joy, nostalgia, envy |
| Secondary Emotions | Emotions that stem from the interplay of primary emotions, cognitive processes, and social factors | Happiness, fear, surprise |
Primary emotions are immediate and instinctive responses to stimuli, universally recognized across cultures. Examples include joy, anger, sadness, fear, surprise, and disgust. These emotions form the foundational aspects of our emotional experiences, arising swiftly and often without conscious thought.
In contrast, secondary emotions are more complex and nuanced. They stem from the interplay of primary emotions, cognitive processes, and social factors. Examples include feelings like jealousy, guilt, or pride. These emotions require a higher level of cognitive interpretation and may vary based on individual experiences and cultural influences.
Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence, often termed EQ, is the ability to recognize, understand, and manage our emotions effectively. [4] It also involves empathizing with others’ emotions. Developing emotional intelligence is crucial in personal and professional life, enabling better relationships and decision-making. It’s a skill that can be cultivated, offering profound benefits in navigating the complex terrain of human emotions.
Understanding Emotions
Emotions are a fundamental aspect of human experience, and understanding them is a multifaceted endeavor that delves into both their linguistic and cognitive dimensions.
The Role of Emotion Language
Emotion language is the bridge that connects our internal emotional experiences with external communication. When we can accurately express our feelings, we convey our state of mind to others and gain a deeper understanding of ourselves. [5] Plus, with a diverse vocabulary of emotions, we articulate ourselves better, fostering empathy and strengthening our relationships with others. The ability to use emotional language is a hallmark of emotional intelligence. It is the factor that is missing in AI. Although we are witnessing the rise of artificial intelligence (AI), the ability to experience emotions enhances our capacity for effective interpersonal communication.
Relationships between Emotions and Intelligence
The interplay between emotions and intelligence is a fascinating area to explore. Emotional intelligence (EQ) complements cognitive intelligence (IQ), enriching our overall mental acumen. [6] With a high EQ empower, individuals can recognize, understand, and manage their emotions effectively. This, in turn, influences decision-making, problem-solving, and interpersonal skills, enhancing their capacity to thrive in both personal and professional spheres.
The Conscious Perception of Feelings
Conscious perception of feelings entails recognizing and acknowledging our emotions consciously. The best way to do this is through meditation and yoga. In fact, if we trace the origins of yoga, we’ll find that early yogis practiced it to achieve a union of body, mind, and soul.
By consciously acknowledging and understanding these emotions, individuals gain the capacity to respond thoughtfully rather than react impulsively. This self-awareness is essential for managing emotions effectively and making informed choices in response to them. [7]
Differences between Feelings and Emotions
While the terms “feelings” and “emotions” are often used interchangeably, they have distinct characteristics. Distinguishing one from another is crucial to decipher the intricacies of our emotional world.
| Aspect | Emotions | Feelings |
| Definition | Immediate, instinctive responses | Complex, conscious interpretations |
| Nature | Rapid, often involuntary | Reflective, influenced by cognition |
| Trigger | Reactions to external stimuli | Interpretations of emotional responses |
| Awareness | Typically automatic | Consciously recognized and processed |
| Response | Precursors to feelings | Consequences of emotional experiences |
| Examples | Fear, anger, joy | Happiness, love, sadness |
Feelings are the conscious perceptions and interpretations of these emotional responses. They involve cognitive processes that add layers of complexity to our emotional experiences.
Emotions are immediate, instinctive responses to stimuli, while feelings are more complex and nuanced interpretations of those emotional responses. Emotions are the raw reactions, and feelings arise as we consciously reflect upon and process these reactions. [8] Understanding this distinction helps us grasp how our emotions manifest and how we consciously interpret and respond to them.
The Evolution of Consciousness
As our species has evolved, so too has our consciousness, allowing for increasingly sophisticated emotional experiences. Our ancestors’ emotional responses were likely more primitive and survival-oriented. As our higher cognitive functions began to develop, we gained the ability to recognize and label our emotions. We started the journey towards self-awareness and gained a deeper understanding of our emotional states. This fascinating interplay highlights the role of emotions in shaping our cognitive experiences and interpersonal connections.
Emotions and Behavior
Emotions serve as powerful motivators of behavior. When we experience emotions, they often trigger actions or reactions. [9] For instance, fear can prompt us to flee from danger, while joy may inspire expressions of happiness. Understanding how emotions influence behavior is crucial in various aspects of life, from personal relationships to professional settings. Emotions can drive our decisions and impact the way we interact with others, making it essential to navigate this intricate connection effectively.
How Emotions Influence Actions
Emotions are catalysts for our actions. When we experience joy, we may engage in activities that enhance that feeling, like celebrating or sharing good news. Conversely, when we are angry, it can drive us to take assertive actions.
Recognizing how emotions influence our actions allows us to make more conscious decisions and navigate life’s complexities.
The Interplay between Thoughts, Emotions, and Behaviors
The interplay between thoughts, emotions, and behaviors is a dynamic cycle. [10] The intricate interplay forms the core of our daily experiences.
Emotions
Emotions are the starting point of the cycle. They arise in response to internal or external stimuli, shaping our initial emotional state.
Thoughts
Emotions trigger thoughts. These thoughts can be automatic and based on our emotional reactions. They influence how we perceive situations and our cognitive responses.
Behaviors
Thoughts, in turn, lead to behaviors. Our actions and reactions are often guided by our thoughts and emotional states. Behaviors can be both physical actions and verbal responses.
Feedback Loop
The cycle is not linear; it’s a feedback loop. Our behaviors can either reinforce our emotional state or lead to new emotional responses, initiating the cycle anew.
Emotions and Learning
Emotions significantly impact our ability to learn. When we’re engaged, curious, or interested, learning becomes more effective. Conversely, negative emotions like anxiety or frustration can hinder the learning process. Exploring the role of emotions in learning helps educators and learners alike create environments that optimize knowledge acquisition and retention, emphasizing the vital link between emotional states and educational outcomes.
The Role of Emotions in Learning Processes
Emotions are integral to the learning journey. They can either enhance or hinder our ability to absorb and retain information. When we experience negative emotions like stress or boredom, it can impede the learning process. [11] Conversely, positive emotions such as curiosity or interest, enhance our capacity to learn and retain information.
The Impact of Emotions on Memory and Attention
Emotions wield a profound influence on memory and attention. Emotional experiences tend to be more memorable, and they can either sharpen or divert our focus. Information tied to emotionally charged experiences tends to be more memorable.
Likewise, our emotional states affect our attention; heightened emotions can either enhance or distract from our focus. Hence optimizing cognitive functions and harnessing emotions can help boost memory and attention.
Emotions in Relationships
Emotions form the cornerstone of interpersonal connections. [12] They influence our perceptions, reactions, and interactions within relationships. Positive emotions, such as love and empathy, contribute to the strength of bonds, while negative emotions, if unaddressed, can strain relationships.
The Influence of Emotions on Interpersonal Relationships
Emotions wield a profound influence on the dynamics of interpersonal relationships. They shape the quality and dynamics of connections with others. Our emotional state determines how we connect with others, influencing communication, empathy, and overall relationship satisfaction.
Strategies to Understand and Manage Emotions in Relationships
Navigating emotions within relationships demands a set of strategies for emotional intelligence. These strategies involve recognizing and understanding one’s own emotions as well as those of others. [13]
| Strategy | Description |
| Self-Awareness | Understand your own emotions and their impact. |
| Active Listening | Listen attentively to others’ emotions and validate them. |
| Empathy | Seek to understand the other person’s perspective and emotions. |
| Effective Communication | Express your emotions openly and encourage open dialogue. |
| Forgiveness | Practice forgiveness for emotional healing and growth. |
These strategies can contribute to a healthier emotional climate within relationships, fostering understanding, resilience, and mutual support.
Conclusion
Emotions are not isolated states but intricate forces that shape our responses to the world around us. Their influence extends to our cognitive functions, memory, attention, and decision-making. Within relationships, emotions form the foundation, influencing our connections with others and the quality of our interactions.
The ability to understand and manage emotions is a fundamental skill that fosters emotional intelligence, promoting healthier, more fulfilling connections with others. By recognizing their influence, we gain insight into our motivations, reactions, and decisions. In relationships, emotions are the compass that guides empathy, communication, and resolution of conflicts.