Table of Contents
Why Should You Care?
Humans have made far more technological advances in the last century than ever before with a constantly increasing rate of progress. As discussed in the previous chapters, AI is quietly working in the background whether we realize it or not. Despite the fact that AI is currently one of the hottest buzzwords with almost all media outlets talking about it, many people still don’t know much about it.
Some consider AI to be a mystery technology that might take all our jobs, while others think that it’s going to solve all the world’s problems. Considering these confusing and often conflicting opinions, it’s important to have a basic understanding of AI because it is soon expected to become large part of our daily lives.
Presently, almost all AI-enabled machines are running on Artificial Narrow Intelligence or limited memory AI, which competes with human intelligence only at specific tasks ranging from spam filters to self-driving cars. But that might change in future and we start seeing ‘more intelligent’ machines with enhanced capabilities sooner than expected.
Will AI Take Over Our Jobs?
That’s one of the most common misconceptions people have about AI and although true to some extent, things are not as bad as the media wants us to believe[i]. It is unbelievably challenging to replicate human intelligence in AI, so instead of asking whether AI will take our jobs, we should be asking how it will change our jobs.
AI-enabled machines are going to be part of our jobs and their main purpose will be to augment our work. Computers are better at processing, storing, and analyzing large datasets. Leaving mundane work to machines will allow humans to focus more on what they are good. Examples include tasks that require creativity, communication, and social skills.
We are still not sure what exactly will be the impact of AI on jobs, but we can expect certain monotonous roles to become obsolete. Some examples of these roles include call center operations, content moderation, document classification, production lines, transportation, packaging, and manufacturing operations support. Highly automatable sectors have already been covered in the previous chapters, which are also the ones most susceptible to job losses.
Will AI Create New Jobs?
Recent advancements in the field of AI have sparked discussions about how AI will supplant workers and increase unemployment. Although the concerns are genuine and understandable, their foundations are not that strong.
Right now, it might be hard to see how AI would create new jobs. However, new technological advances are not something new and nonstop progress has been made for the last 250 years. Despite this progress, the unemployment rate in the United States on average has stayed almost the same, between 5% to 10%.
Automated Teller Machines are a good example in this context. There are more tellers now than ever before. Since ATMs can do the mundane tasks and lower the overall costs, banks opened more branches and hired more tellers. Similarly, AI will also create other types of new jobs and experts even predict that AI is going to be the biggest job engine. Contrary to the popular belief that AI will destroy jobs, it will create millions of new jobs, many of which we cannot yet fully visualize.
Data[ii] from the US Bureau of Labor Statistics shows a high demand for human translators. If AI takes over basic translation, the translation costs will drop significantly and so will the cost of doing business with foreigners. This will provide incentive to businesses that want to go global, creating more jobs, including jobs for advanced human translators.
According to a report[iii] by the World Economic Forum, by 2022, a total of 50 million new jobs will be created by AI, and the demand for new roles will counterbalance the decrease of demand for old roles. However, the transition will still be difficult for millions of employees and businesses need to prepare their workforce by upskilling and reskilling their workforce and taking a proactive approach.
Robots vs. AI
The purpose of robots is to get work done in less time than humans with better efficiency. Robots can be autonomous or semi-autonomous. AI, on the other hand, is a field of computer science that deals with developing advanced software, or the ‘brain,’ that runs inside something like a robot. Robots are like containers that can be both AI-enabled and non-AI-enabled.
Robots are merely a container or body of AI and don’t always mimic the human form. A good example is Siri, she is an AI with no robotic container. AI is the brain inside a robot, which can be programmed to do certain tasks and is equipped with sensors like cameras and motion sensors[iv]. Although researchers have given robots the sense of sight via cameras, hearing via mics, and sense of taste and smell via chemical sensors, robots still lack what we call the sixth sense.
Humans have this sixth sense, also called proprioception, which refers to our awareness about our body parts and muscles. Progress is being made in this regard too using sensory materials and ML algorithms that enable robots to detect touch, but it’s still far from being perfect. Steady progress is being made in robotics/AI-controlled robots are these advances have a potential to work wonders in the future.
Is AI Dangerous?
This is another question that frequently pops up when talking about AI. Unfortunately, the public usually answers this question in the context of sci-fi movies. We are still far from developing hyper-intelligent computers and killer robots. The answer to the question ‘is AI dangerous’ is complicated. On one hand strong AI has the potential to help humans eradicate diseases, wars, and poverty, while on the other hand there are significant dangers.
We don’t have to worry much about AI in its current form, but there are risks even at the level of weak AI[v]. For example, unauthorized access of AI-enabled military equipment can wreak havoc on our planet. On a micro level, if a hacker gets control of a thermostat system, he or she can create a health hazard for others. Similarly, security breach of autonomous vehicles or a city management system can also create chaos in the whole city.
The technology itself does not cause serious concerns. But the fact that it’s the humans who have to initially program AI that worries experts. Other than the talked about existential risks, some examples of potential dangers of AI include:
AI Can Be Programmed to Be Dangerous
Humans can intentionally program AI to cause harm, which is also applicable to AI in its current form. Examples include missile defense systems, military robots, and drones. Once started, the fail-safe mechanisms of autonomous weaponry are very difficult to stop, causing humans to lose control and further escalate the situation.
AI Can Develop Destructive Methods
AI might develop destructive methods to complete a task. For example, an AI-powered self-driving car might start breaking traffic signals or even start running over pedestrians if you ask it to reach the airport as quickly as possible. Things can get even worse when it comes to super-intelligent machines of the future. Potential climate control or geo engineering systems can have a catastrophic effect on ecosystems and infrastructure.
Social Manipulation
Advanced AI algorithms have proved to be very effective at marketing and advertising, but the technology can also be used for social manipulation. Social media platforms already know who we are, what we do, how and when we do certain things, what we like, and people close to us.
Investigations are still going on to uncover how social media used information to influence outcomes of the 2016 US presidential elections and the Brexit referendum. Regardless of the outcomes of the investigations, social media platforms have the power to influence our opinions and can be used for social manipulation.
Social Grading and Invasion of Privacy
Many countries like China are already using social grading systems that judge people based on predefined criteria. These systems even know how much time an individual spends playing video games and whether or not they jaywalk. Humans are complex beings and some variables are not enough to define who we truly are.
Then there are systems that can track and analyze moves of individuals at scale using CCTV cameras, facial recognition algorithms, and information from social media. In addition to being an invasion of privacy, Governments with access to this level of information can turn into social oppression.
Discrimination, AI Bias
Businesses and organizations can use the large amounts of information available to AI systems against us. For example, an employer might reject your job application based on your ‘social credit score’. There is always a chance of someone misusing a powerful technology and the available data. Although AI is being used for a lot of good purposes like medical diagnosis, it can also be used towards malicious ends.
AI algorithms can have bias built-in as they are developed by humans. If the algorithm and the data in the training sets is biased, the end result will also be biased, which can lead to unintended outcomes. One small example of this is Tay, Microsoft’s Twitter chatbot that became racist in less than 24 hours. When people started tweeting it with racist sentiments, the bot ‘learnt’ and started tweeting similar sentiments to them.
Physical Safety and Accidents
Imperfections in AI systems can cause accidents and it still remains a challenge to determine who is responsible. For example, if a self-driving car gets into an accident, who would be responsible: the programmer, the car manufacturer, or the owner? If the manufacturer is free of accountability, it might not have any incentive to design safer products and prioritize safety over user preferences.
Benefits of AI
The last chapter covered numerous applications of AI that are revolutionizing different sectors. The benefits of AI are common and applicable to almost all industries covered before. AI offers a lot of benefits to humanity, including the economy, industries, and the justice system. Some major benefits of AI are as follows[vi]:
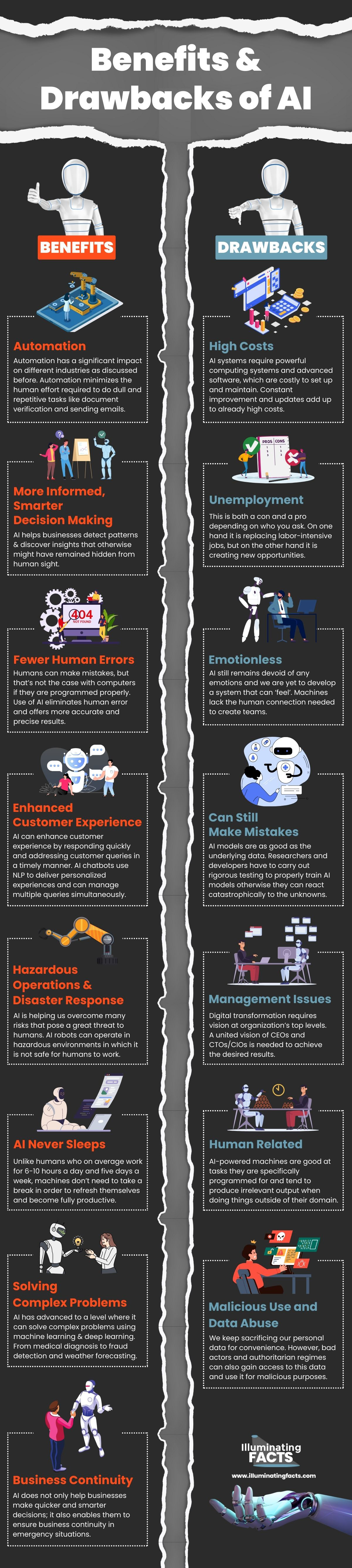
Automation
Automation has a significant impact on different industries as discussed before. It not only leads to increased production rates and improved productivity, it also enables businesses and organizations to use raw materials more efficiently, improve product quality, reduce lead times and improve safety.
Automation minimizes the human effort required to do dull and repetitive tasks like document verification and sending emails. AI-powered robotic process automation tools allow different departments including HR, marketing, IT, and sales to execute monotonous activities quickly and greatly improve employee productivity.
More Informed, Smarter Decision Making
AI helps businesses detect patterns and discover insights that otherwise might have remained hidden from human sight. From trend analysis to data delivery coordination, forecasting and quantifying uncertainties, AI is helping organizations make the best possible and more informed decisions based on the available data.[vii] Unless intentionally programmed to simulate human emotions, AI delivers insights that are free from bias.
AI also speeds up the decision-making process as machines can process data a lot faster than humans. It’s almost impossible for regular chess players to beat computers in the game because AI makes the best possible steps. Reduction in the time required to make an informed decision can prove to be a competitive advantage in today’s ultra-competitive markets.
Fewer Human Errors
Humans can make mistakes, but that’s not the case with computers if they are programmed properly. Use of AI eliminates human error and offers more accurate and precise results. AI-enabled systems are not prone to data entry mistakes, which is especially beneficial for sectors like banks that cannot afford to make any such mistakes. Another example is weather forecasting in which use of AI minimizes human error and provides more accurate forecasts.
Enhanced Customer Experience
AI can enhance customer experience by responding quickly and addressing customer queries in a timely manner. AI chatbots use NLP to deliver personalized experiences and can manage multiple queries simultaneously. AI takes care of the boring tasks and enables the customer services reps to focus more on complex queries and delivering exceptional customer service.
Hazardous Operations and Disaster Response
AI is helping us overcome many risks that pose a great threat to humans. AI robots can operate in hazardous environments in which it is not safe for humans to work[viii]. Whether it’s going to mars, mining coal, exploring the oceans, or defusing a bomb, AI-assisted robots are effective when it comes to working in unsafe conditions and can be a great resource in disasters.
Due to extreme weather events like wildfires, a growing number of government and private organizations are embracing AI to manage such situations. Another benefit of AI in this regard is their use in wars. AI-powered robots are expected to take an active role in future wars instead of putting humans in the firing line.
AI Never Sleeps
Unlike humans who on average work for 6-10 hours a day and five days a week, machines don’t need to take a break in order to refresh themselves and become fully productive[ix]. Machines also don’t have to spend a lot of time getting ready and maintaining themselves. They are designed to work 24/7 at peak performance, don’t get bored, and keep going without any human intervention. This enables organizations to maintain critical services and reduce errors while maintaining a high level of accuracy.
Solving Complex Problems
AI has advanced to a level where it can solve complex problems using machine learning and deep learning. From medical diagnosis to fraud detection and weather forecasting, AI is helping organizations solve industry-specific problems and develop the right solutions. AI-powered systems are efficient in sifting through huge piles of data and extracting actionable insights that help increase productivity and efficiency, and reduce expenses.
Business Continuity
AI does not only help businesses make quicker and smarter decisions; it also enables them to ensure business continuity in emergency situations. Risk management is among the most important applications of AI, which helps businesses prepare and proactively respond to crises[x].
Drawbacks of AI
Every technology has a darker side and AI is no exception. Unforeseen outcomes are at the top of the list. AI should be applied to solve problems that have ‘black and white’ outcomes and clear procedures[xi]. Too many unknowns make it difficult to apply AI, which is one of the reasons why the technology still hasn’t fully matured yet. The main drawbacks or cons of AI include:
High Costs
AI systems require powerful computing systems and advanced software, which are costly to set up and maintain. Constant improvement and updates add up to already high costs[xii]. Businesses need plenty of time, and financial and human resources to operate AI systems. Although cloud delivery and subscription services allow users to quickly get started without having to heavily invest in the underlying infrastructure, they are still expensive in the long run, especially for small and medium sized businesses.
Unemployment
This is both a con and a pro depending on who you ask. On one hand it is replacing labor-intensive jobs, but on the other hand it is creating new opportunities. Businesses are always looking for ways to cut costs, and AI provides them with a great opportunity to achieve their desired results. AI will create millions of new jobs, but it will also displace millions of old ones and the transition won’t be easy for everyone[xiii].
Emotionless
AI still remains devoid of any emotions and we are yet to develop a system that can ‘feel’. Machines lack the human connection needed to create teams. Lack of ability to bond with humans makes machines fail at certain tasks like social bonding, communication, and team management. That’s the main reason AI is still only good for taking care of mundane tasks that do not require emotional intelligence because the lack of emotions can become daunting at certain times.[xiv]
Can Still Make Mistakes
AI models are as good as the underlying data. Researchers and developers have to carry out rigorous testing to properly train AI models otherwise they can react catastrophically to the unknowns. We still hear news of self-driving cars crashing into pedestrians because they were unable to ‘see’ worn lines or failed to distinguish a picture from a real person. Without large amounts of training data and repeating the unknowns over time, AI-powered machines will keep repeating the same mistakes.
Management Issues
Digital transformation requires vision at organization’s top levels. A united vision of CEOs and CTOs/CIOs is needed to achieve the desired results. That’s the reason smaller and more nimble business models built around AI are technologically more successful than large enterprises that lack vision, knowledge, and ability to leverage AI’s capabilities.
Human Related
AI-powered machines are good at tasks they are specifically programmed for and tend to produce irrelevant output when doing things outside of their domain. AI still requires human intervention to complete complex tasks, is not as adaptable as humans and balks in the face of constant change.
Although AI in its current form is helping humans in different tasks, that can change in future and we might become too dependent on them. With automation at its core, AI can make humans lazy, which can become a problem for future generations. Too much dependence on machines can erode human capabilities, creativity, and their ability to think, and communicate effectively.
Most AI tools are in the hands of businesses looking to improve efficiency and profitability. Ethics and values are often not embedded into these tools, which they use to make important decisions. These tools and systems are also not easy to regulate, which means their owners can abuse data to their advantage and exercise power using it[xv].
Malicious Use and Data Abuse
We keep sacrificing our personal data for convenience. However, bad actors and authoritarian regimes can also gain access to this data and use it for malicious purposes. Deep fakes are one example of how bad actors can use content to their advantage and make it difficult for us to distinguish between what is real and what is fake.
Some other examples of data abuse and malicious uses include AI malware, AI-cloud services abuse, Smart Assistants abuse, AI-assisted password guessing, AI and machine learning assisted CAPTCHA breaking, AI-assisted encryption, human impersonation, online game cheats, AI-assisted hacking, social engineering, abuse of image recognition systems, AI-assisted stock market manipulation, and AI-assisted ransomware.[xvi]
Conclusion
AI has a great potential for making this world a better place to live and has its own advantages and drawbacks. Regardless of the pros and cons, its impact on global industries is undeniable. Excess of everything is dangerous and powerful tools in the hands of wrong people can have disastrous results.
AI technologies are evolving steadily. Researchers need to make sure AI does not get out of hand. It’s not possible to accurately predict the future outcomes of advances in the field, so we need to stay optimistic and prepare to embrace AI in our daily lives instead of getting paranoid about its future implications.
[i] “The Impact of Artificial Intelligence – Widespread Job Losses”. Retrieved from https://www.iotforall.com/impact-of-artificial-intelligence-job-losses
[ii] “Occupational Outlook Handbook – Interpreters and Translators”. Retrieved from https://www.bls.gov/ooh/media-and-communication/interpreters-and-translators.htm
[iii] “The Future of Jobs Report – World Economic Forum Centre for the New Economy and Society”. https://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_Future_of_Jobs_2018.pdf
[iv] “What’s the Difference Between Robotics and Artificial Intelligence?”. Retrieved from https://blog.robotiq.com/whats-the-difference-between-robotics-and-artificial-intelligence
[v] “Is Artificial Intelligence Dangerous? 6 AI Risks Everyone Should Know About”. Retrieved from https://www.forbes.com/sites/bernardmarr/2018/11/19/is-artificial-intelligence-dangerous-6-ai-risks-everyone-should-know-about/?sh=5f4102f52404
[vi] “Advantages and Disadvantages of Artificial Intelligence”. Retrieved from https://towardsdatascience.com/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-artificial-intelligence-182a5ef6588c
[vii] “Top 10 Benefits of Artificial Intelligence (AI)”. Retrieved from https://www.10xds.com/blog/benefits-of-artificial-intelligence-ai/
[viii] “Advantages and Disadvantages of Artificial Intelligence”. Retrieved from https://towardsdatascience.com/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-artificial-intelligence-182a5ef6588c
[ix] “7 Benefits of AI That Will Help Humanity, Not Harm It”. Retrieved from https://interestingengineering.com/7-ways-ai-will-help-humanity-not-harm-it
[x] “AI and Business Continuity: A Future Resilient Environment”. Retrieved from https://www.prontorecovery.com/blog/ai-and-business-continuity-a-future-resilient-environment/
[xi] “A Look at the Downsides of Artificial Intelligence”. Retrieved from https://www.reworked.co/information-management/a-look-at-the-downsides-of-artificial-intelligence/
[xii] “Advantages and Disadvantages of Artificial Intelligence”. Retrieved from https://www.simplilearn.com/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-artificial-intelligence-article
[xiii] “The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Unemployment”. Retrieved from https://www.technology.org/2019/12/17/the-impact-of-artificial-intelligence-on-unemployment/
[xiv] “10 Advantages and Disadvantages of Artificial Intelligence”. Retrieved from https://www.analytixlabs.co.in/blog/advantages-disadvantages-of-artificial-intelligence/
[xv] “Ethics of AI: Benefits and risks of artificial intelligence”. Retrieved from https://www.zdnet.com/article/ethics-of-ai-the-benefits-and-risks-of-artificial-intelligence/
[xvi] “Malicious Uses and Abuses of Artificial Intelligence”. Retrieved from https://documents.trendmicro.com/assets/white_papers/wp-malicious-uses-and-abuses-of-artificial-intelligence.pdf